In life sciences analysis, RNA modifications operate like “molecular switches” in gene expression, controlling how and when cells produce proteins.
One of the commonest RNA modifications is m6A(N6-methyladenosine), which impacts RNA stability and the effectivity of protein synthesis. It has been intently linked to mobile operate and even illness improvement.
For a very long time, this area has confronted a significant problem: inconsistent outcomes throughout laboratories.
For the identical gene and nucleotide web site, one paper might report a modification whereas one other exhibits none. These inconsistencies make it troublesome for researchers to find out which modifications are real and reproducible.
Now, this confusion might lastly be resolved.
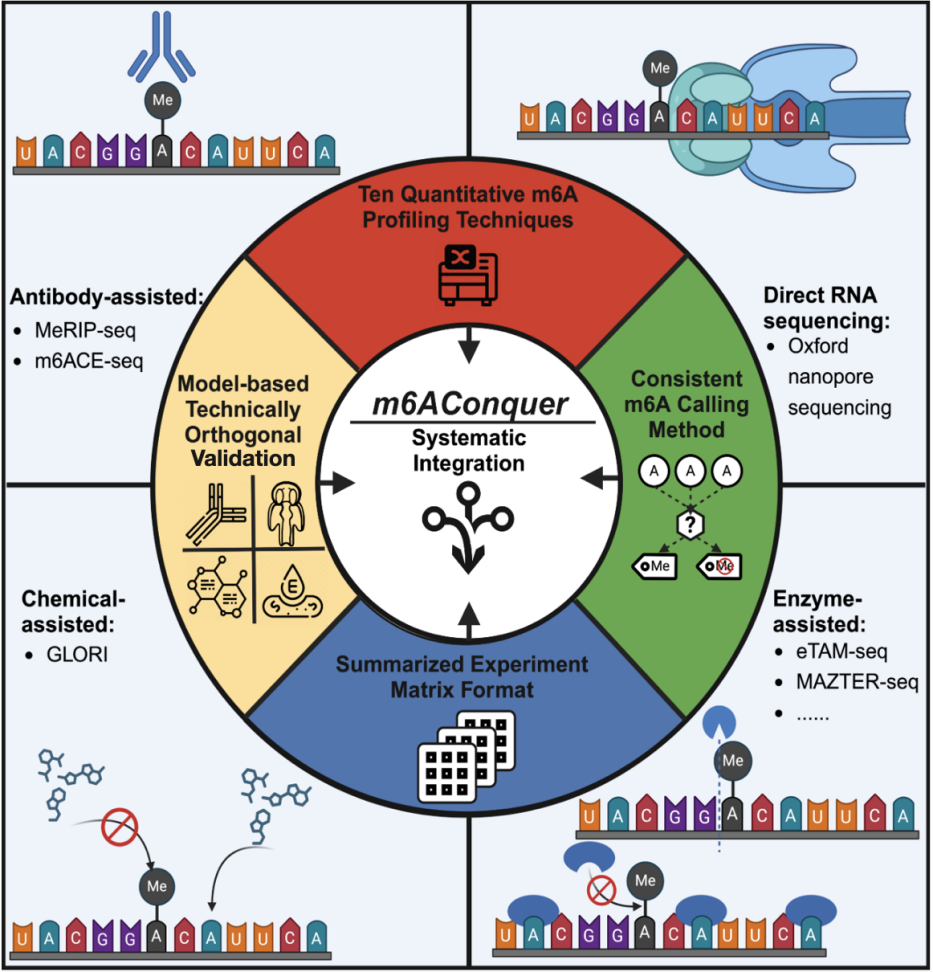
Figure 1 m6AConquer: A knowledge-sharing platform enabling constant quantification and orthogonal validation throughout ten m6A modification detection applied sciences
A unified customary
Recently, Dr Zhen Wei and his team from the Department of Biological Sciences and Bioinformatics at Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University, along with researchers from the University of Liverpool, revealed their newest findings within the worldwide journal Nucleic Acids Research. They launched m6AConquer, the world’s first database that integrates a number of m6A detection strategies and verifies outcomes utilizing orthogonal, impartial strategies to make sure reproducibility.
“In the past, researchers each had their own experimental system. Now we finally have a shared coordinate system that aligns all the data,” says Dr Wei.
Simply put, m6AConquer consolidates m6A sequencing knowledge from 10 experimental applied sciences and lots of of public datasets. It employs an algorithm for orthogonal validation, filtering for modification websites which might be reproducibly detected throughout strategies with distinct biochemical rules.
This means researchers now have entry to a dependable, unified, and verifiable benchmark dataset.
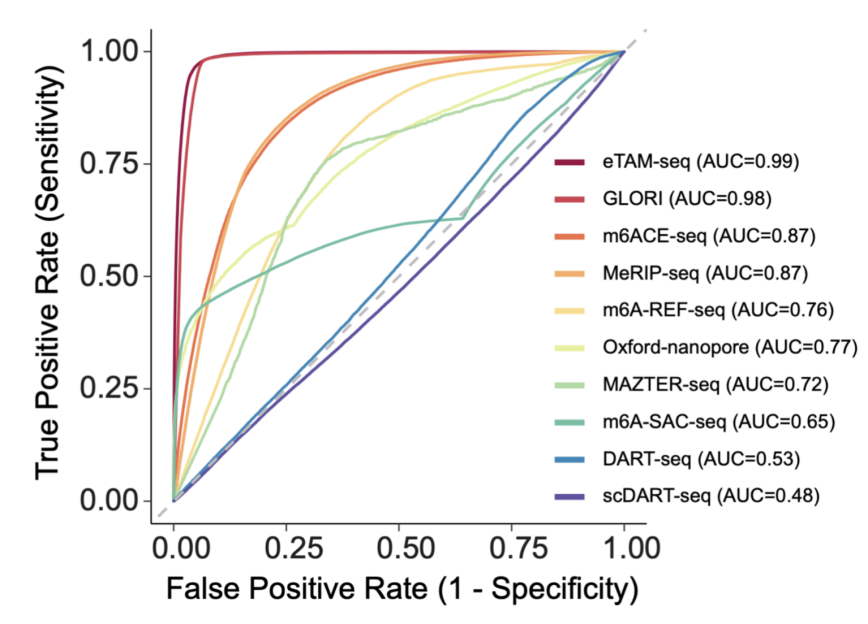 Figure 2 makes use of orthogonally validated m6A websites as floor reality to precisely consider the efficiency of varied m6A detection strategies.
Figure 2 makes use of orthogonally validated m6A websites as floor reality to precisely consider the efficiency of varied m6A detection strategies.
A software for authenticating RNA modifications
m6AConquer could be seen as a “detector” for verifying RNA modifications.
It helps scientists distinguish between reproducible organic alerts and random experimental noise.
The analysis team adopted the statistical framework used within the internationally recognised ENCODE challenge. This contains the IDR mannequin, which measures whether or not completely different strategies constantly detect the identical RNA modification websites, making certain dependable outcomes. Ultimately, they recognized greater than 135,000 high-confidence m6A modification websites (IDR
“This is the first time a rigorous ground truth dataset has been established in this field,” says Dr Wei. “It allows researchers to evaluate the performance of various m6A detection methods using a shared, validated reference. As a result, there is no longer a need to adjust for methodological differences. This greatly enhances consistency and reproducibility in research and provides a reliable data standard for future algorithm development and disease biology research.”
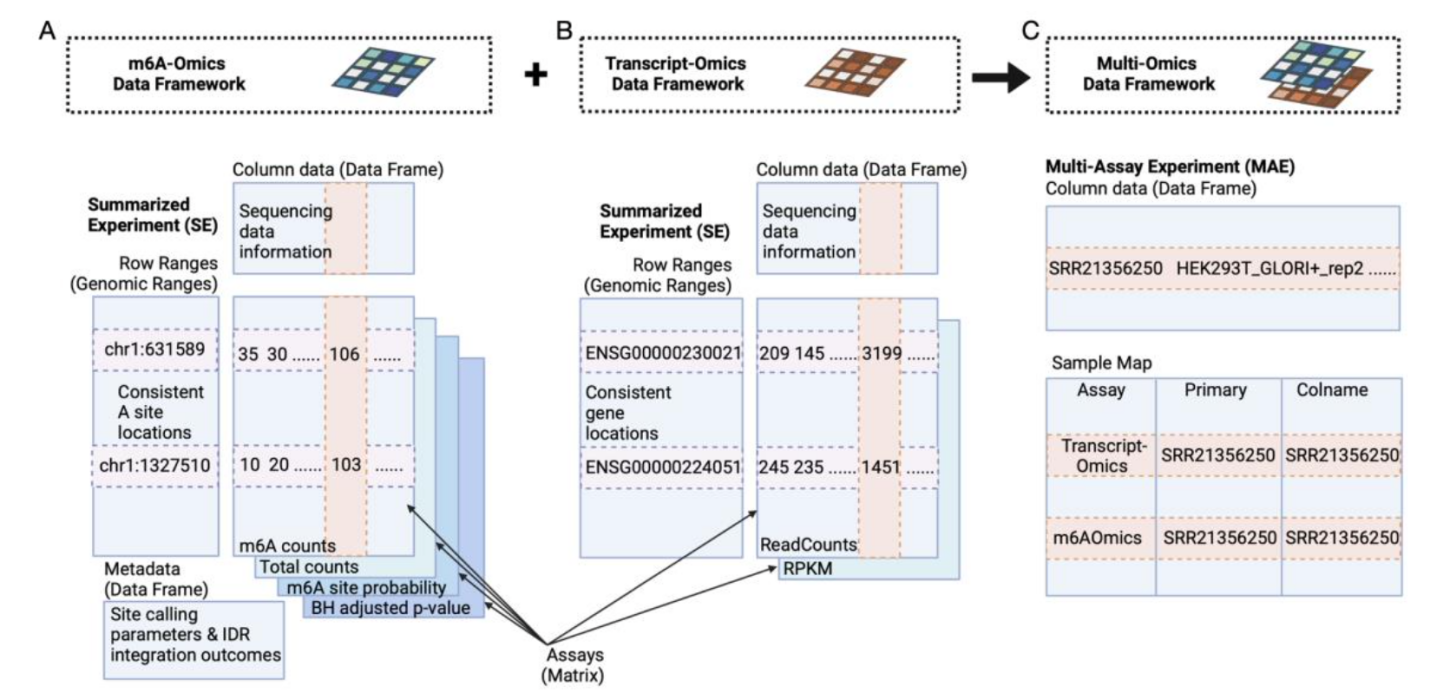
Figure 3: The Multi-Omics Data-Sharing Framework Developed by m6AConquer
From usable to user-friendly
Beyond making certain knowledge reliability, Dr Wei’s team additionally centered on usability – making the info extra accessible to scientists.
m6AConquer has established a standardised data-sharing framework that restructures beforehand scattered and sophisticated multi-omics uncooked knowledge, capturing a number of layers of knowledge derived from the high-throughput m6A profiling experiments, into “analysis-ready” matrix codecs.
This is akin to integrating dictionaries from completely different international locations into one shared language. Researchers now not must spend intensive time cleansing and aligning knowledge. They can immediately start comparisons, modelling and validation, considerably bettering analysis effectivity and reproducibility.
A brand new window into genetic variation and illness mechanisms
Even extra promising is that m6AConquer not solely integrates RNA modification knowledge but in addition hyperlinks RNA modifications to genetic variation, gene expression, and illness threat.
The analysis team recognized over 6,000 genetic variants considerably related to the modification ranges of high-confidence m6A websites – often known as m6A QTLs. These findings reveal how genetic variations might affect RNA modifications and, in flip, alter gene regulation.
Some of those variants are situated in threat areas related to advanced ailments akin to psychiatric issues and melancholy, providing new insights into their molecular mechanisms.
“This means we’re not only observing the ‘results’ of RNA modifications, but beginning to understand their underlying ‘causes’,” explains Dr Wei. “Some genetic mutations may affect disease risk precisely by altering RNA modification levels.”
Dr Wei provides that m6AConquer will not be solely a knowledge useful resource but in addition a bridge connecting genetic variation, RNA modifications, and illness improvement. It additionally lays a stable basis for future purposes akin to synthetic intelligence modelling, biomarker identification for illness analysis, and drug goal discovery utilizing high-confidence knowledge.
“We hope this open-access resource will serve as a key step in advancing epitranscriptomics research, the study of chemical modifications on RNA that regulate its function, from data integration to mechanistic understanding,” he says.
The m6AConquer database and all related analytical instruments are freely out there to researchers worldwide at: rnamd.org/m6aconquer
Translation:Luyao Wang
Editor:Patricia Pieterse
