Ultracold atoms, chilled to temperatures simply above absolute zero, symbolize a strong frontier in each basic physics and rising applied sciences. Louise Wolswijk, Luca Cavicchioli, and Giuseppe Vinelli, alongside their colleagues, current a complete overview of the strategies scientists now make use of to harness the distinctive properties of those atoms. Their work particulars how researchers entice, manipulate, and probe these quantum techniques, enabling precision measurements, advanced simulations, and doubtlessly revolutionary advances in data processing. This tutorial supplies a necessary useful resource for newcomers to the sector, outlining the experimental toolkit that drives present analysis and guarantees to unlock additional breakthroughs in science and know-how.
Cold Atom Cooling and Trapping Techniques
Researchers have developed a complete toolkit for creating and manipulating chilly atomic samples, enabling research of quantum mechanics and the event of superior applied sciences. Techniques equivalent to Doppler cooling gradual atomic movement to millikelvin temperatures, whereas sub-Doppler cooling achieves even decrease temperatures. Magneto-optical traps concurrently cool and entice atoms, providing excessive seize velocity, whereas magnetic traps present excessive depth. Optical dipole traps make the most of far-off-resonance gentle to create versatile and tailor-made potentials, and optical lattices create periodic potentials for top controllability.
These strategies supply distinctive strengths and limitations, impacting purposes like atomic clocks, quantum transport, and the examine of many-body physics. This work particulars the energy of dipolar interactions in varied atomic and molecular species, together with rubidium, chromium, erbium, dysprosium, and a number of other molecules. Parameters equivalent to dipole second and interplay energy are essential for understanding many-body physics, creating novel quantum phases, and constructing quantum simulators. Furthermore, researchers have developed strategies for controlling the quantum states of atoms, together with Bragg transitions, Rabi and Ramsey strategies, Raman transitions, and the creation of artificial gauge fields, important for quantum computing, precision spectroscopy, atomic clocks, and metrology. Finally, the work summarizes strategies for detecting atoms and measuring their quantum states, encompassing ensemble detection strategies like absorption and time-of-flight imaging, in addition to state-selective detection strategies like Stern-Gerlach separation and optical pumping. Quantum fuel microscopes allow site-resolved imaging of atoms in optical lattices, offering a precious useful resource for researchers within the discipline.
Laser and Evaporative Cooling to Nanokelvin Temperatures
Researchers have pioneered a complete toolkit for manipulating matter at temperatures close to absolute zero, enabling basic research of quantum mechanics and the event of superior applied sciences. The course of begins with laser cooling, which slows atomic movement, adopted by trapping atoms utilizing magnetic and optical fields to realize microkelvin temperatures. This culminated within the creation of the primary Bose-Einstein condensate in 1995, a landmark achievement. Subsequent improvement of evaporative cooling strategies additional decreased temperatures to the nanokelvin scale, enhancing the precision of experiments and permitting for the creation of quantum degenerate Fermi gases.
The staff engineered tightly confining traps, each magnetic and optical, to realize excessive atomic densities in each actual and part house, essential for observing collective quantum phenomena. A big development concerned the creation of optical lattices, periodic potentials fashioned by interfering laser beams, which function exactly managed environments for learning many-body physics. Researchers additionally harnessed Feshbach resonances, permitting them to tune interatomic interactions and observe the superfluid-Mott insulator transition in Bose gases and the Bose-Einstein condensate to Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer crossover in Fermi gases. These strategies enabled the creation of dipolar quantum gases and the exploration of extremely excited Rydberg states, increasing the vary of accessible bodily phenomena.
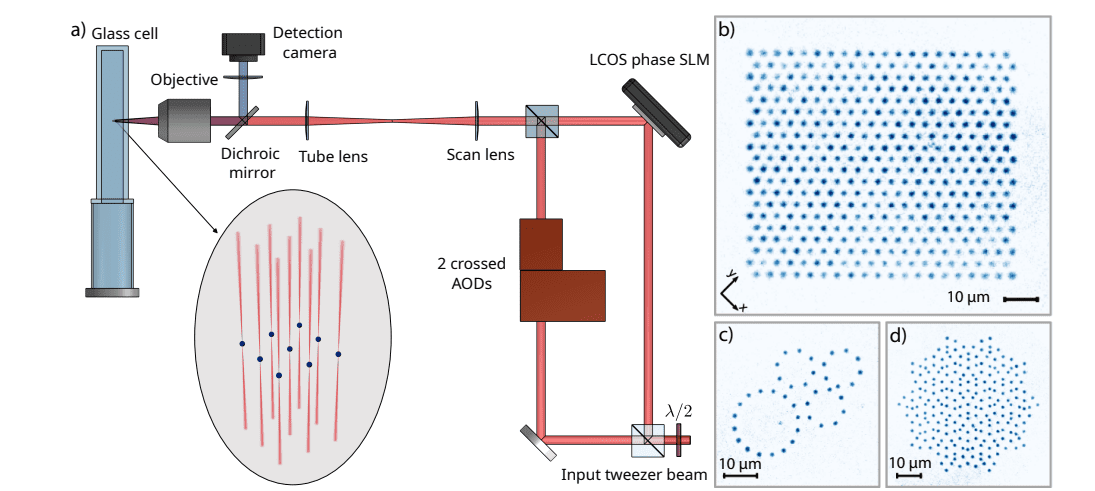
To obtain even larger management and determination, scientists developed quantum fuel microscopes able to imaging particular person atoms inside optical lattices, permitting for the examine of single-site properties and the remark of advanced quantum correlations. Furthermore, researchers engineered artificial gauge fields and spin-orbit coupling in ultracold atoms, opening new avenues for simulating topological phases and gauge theories. More lately, the event of optical tweezer arrays and large-scale programmable Rydberg quantum simulators has enabled the creation of advanced quantum techniques with unprecedented management, paving the way in which for the event of near-term quantum computer systems and superior quantum simulations.
Ultracold Atom Control and Laser Cooling Techniques
Researchers have achieved exceptional developments in manipulating and controlling atoms at near-absolute zero temperatures, establishing a strong toolkit for basic mechanics research and rising applied sciences. This work particulars a complete set of strategies for trapping, cooling, and detecting ultracold atoms, enabling exact management over their quantum conduct. The basis of this management lies in laser cooling, the place atoms are slowed utilizing gentle, reaching temperatures within the millikelvin vary or under. Building upon laser cooling, scientists make use of varied trapping strategies to restrict these ultracold atoms.
Magneto-optical traps (MOTs) concurrently cool and confine atoms, whereas magnetic traps make the most of weak magnetic fields to carry atoms. Optical dipole traps, and their extra refined kind, optical tweezers, confine atoms on the focus of far-detuned laser beams, even enabling the trapping of single atoms in reconfigurable arrays. A very highly effective method includes optical lattices, created by interfering counter-propagating laser beams, which confine atoms in a periodic potential, serving as a platform for quantum simulations. To attain even decrease temperatures, evaporative cooling is employed, selectively eradicating the best power atoms from a entice, lowering the general temperature of the remaining cloud. Furthermore, miniaturization of those setups is achieved by using atom chips, paving the way in which for extra compact and built-in units. Sub-Doppler cooling strategies additional refine temperature management by exploiting atomic transitions and polarization gradients.
Ultracold Atoms Advance Quantum Science and Technology
This work comprehensively evaluations the established and rising strategies used to control and detect ultracold atoms, demonstrating the sector’s central position in advancing each basic science and technological innovation. Researchers have developed exact strategies for cooling, trapping, and controlling impartial atoms, enabling the examine of quantum phenomena and the creation of novel quantum applied sciences. These strategies underpin investigations into strongly interacting quantum matter, many-body physics, topological phases, and dynamics removed from equilibrium, providing distinctive insights into advanced bodily techniques. The convergence of superior management strategies, strong detection schemes, and large-scale engineering is poised to additional lengthen the frontiers of ultracold atom analysis. While acknowledging the present state-of-the-art, the authors spotlight ongoing improvement in areas equivalent to high-resolution imaging with giant tweezer arrays, hybrid imaging techniques, and single-particle-resolved detection for quantum processors and networks. These developments promise to reinforce precision measurements and facilitate the scaling of quantum applied sciences for computation, communication, and metrology.