Technology is a supply of a nation’s energy. In 2023, Global Finance ranked the Republic of China (Taiwan) third on the earth in technological development, behind South Korea and the United States. Yet, Taiwan was not all the time at the forefront of international technological growth. According to Professor of Economics Peter C.Y. Chow at City University of New York, former President Tsai Ing-wen (蔡英文) got here into workplace in 2016 in a interval of financial slowdown for Taiwan, which had begun within the mid-Nineties and accelerated in the course of the 2008 international monetary disaster. During that interval, the rise of China had pushed Taiwan to the margins of worldwide financial exercise and excluded it from a lot of worldwide financial deliberation. In this unfavorable international financial surroundings, the Tsai Administration sought to revitalize Taiwan’s financial system by means of superior expertise.
In her first inaugural address on May 20, 2016, Tsai framed the promotion of nationwide industries as half of Taiwan’s “New Model for Economic Development.” She stated: “We will prioritize our plans to promote five major innovative industries, with the goal of reshaping Taiwan’s global competitiveness.” These sectors—biomedicine, inexperienced power expertise, sensible equipment, nationwide protection, and the Asia Silicon Valley—are all high-tech industries. Tsai’s authorities later included two further industries—the brand new agriculture and the round economies—within the plan, which grew to become the 5+2 Industrial Innovation Plan (5+2產業創新計畫). In Tsai’s second time period, she launched her second flagship plan, the Six Core Strategic Industries (六大戰略產業), which additionally integrated burgeoning sectors reminiscent of cybersecurity. In executing these two initiatives, the Tsai Administration left an indelible mark on Taiwan’s thriving high-technology industries.
How are Taiwan’s Technology Policies Formed?
According to the National Science and Technology Council (NSTC, 國家科學及技術委員會), Taiwan’s expertise insurance policies are primarily formulated by means of 4 mechanisms: 1) the Executive Yuan’s (行政院) main insurance policies and applications; 2) resolutions of the Executive Yuan’s Board of Science and Technology (BOST, 行政院國家科學技術發展委員會); 3) the “National Science and Technology Conference,” held each 4 years by the NSTC; and 4) the planning and implementation by all ministries and councils in keeping with their capabilities as outlined by regulation.
These mechanisms had been codified beneath the Fundamental Science and Technology Act (科學技術基本法), enacted on January 20, 1999—which serves because the authorized foundation for expertise coverage formulation. According to Article 1 of the Act, the basic tips and ideas for the federal government in selling scientific and technological growth are to 1) to lift the requirements of science and expertise, 2) keep financial growth, 3) strengthen ecological preservation, 4) enhance public well-being, 5) enhance nationwide competitiveness, and 6) promote the sustainable growth of human society. On the entire, the Act targeted on creating abilities in science and expertise fields in tandem with humanities and social science—by means of help to public colleges, institutes and enterprises, the formulation of the National Science and Technology Plan, and the event of scientific and technological personnel. One energy of the Act lay in its concentrate on ecological preservation. However, it had shortcomings when it got here to the promotion of public-private partnerships, which additionally play a key function in technological growth.
On September 8, 2016, the Tsai Administration accepted the Asia Silicon Valley Development Plan (2016-2020) (亞洲·矽谷計畫) as a strategy to join Taiwan with high-tech analysis and growth (R&D) communities worldwide, together with attracting and retaining shiny expertise to construct a complete progressive startup ecosystem. The plan known as for the institution of an progressive R&D middle, in addition to the promotion of connections with Silicon Valley and different innovation communities. Taiwan’s expertise R&D spending as a ratio of gross home product (GDP) reached new data in the course of the first time period of the Tsai Administration, rising from 3.09 percent in 2016 to 3.63 percent in 2020. The non-public sectors contributed essentially the most to this enhance—offering 71.3 percent of complete R&D spending in 2020. This statistic reveals the vital partnership between non-public enterprise and the federal government in shaping Taiwan’s expertise capability.
The 5+2 Industrial Innovation Plan
Unlike present President Lai Ching-te (賴清德)’s the Five Trusted Industry Sectors Promotion Plan (五大信賴產業推動方案), which emphasizes an indispensable and trusted technological companion of democracies all over the world, the 5+2 Industrial Innovation Plan, because the flagship program of the Tsai authorities, aimed to develop the human capability of Taiwan’s innovation-related non-public sectors. The 5+2 Industrial Innovation Plan incorporates four major strategic components that had been to: 1) foster interdisciplinary expertise within the digital financial system, 2) reinforce technical professional coaching mechanisms for industries, 3) diversify profession paths to invigorate the cultivation of high-caliber scientific analysis professionals, and 4) recruit and retain worldwide prime expertise. Put succinctly, the plan targeted on revitalizing professional coaching mechanisms and enhancing particular person expertise, together with expertise from overseas. According to a 2017/2018 ManpowerGroup Talent Shortage Survey, the job vacancies in Taiwan that had been the toughest to recruit for had been gross sales representatives, adopted by engineers and IT technicians. Therefore, with a rising pool of expertise expertise, Taiwan may higher reply to the challenges of these expertise shortages in Taiwanese industries.
Under the 5+2 Industrial Innovation Plan, the Executive Yuan additionally initiated the Smart Machinery Development Plan (智慧機械產業推動方案規劃) on July 21, 2016 to improve Taiwan’s equipment trade. The program makes use of the potential of Industry 4.0 applied sciences—cloud computing, massive knowledge, the Internet of Things (IoT), and sensible robots. Under these circumstances, the BOST and the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST, 科學技術部) set a objective for the National Science and Technology Development Plan (2017-2020) (國家科學技術發展計畫) to transition Taiwan in the direction of an innovation economy. [1]
Taiwan’s Ministry of Economic Affairs (MOEA, 經濟部) elaborated on the Smart Machinery Development Plan in a 2017 white paper, titled Taiwan Key Innovative Industry—Smart Machinery. The paper outlined three areas by means of which to advertise Taiwan’s progressive industries: 1) sensible equipment expertise, 2) cultivating expertise for the sensible equipment trade, and three) the sensible equipment trade promotion program. In the primary space, core and application technologies of smart machinery can be developed in keeping with the promotion of Industry 4.0 applied sciences. In the second space, the Taiwanese authorities would earmark an estimated USD 70 million funding in the Central Taiwan Science Park and the Southern Taiwan Science Park, to construct an clever self-manufacturing website, domesticate new enterprises, and practice skilled researchers. In the third space, the Executive Yuan would approve the institution of a Smart Machinery Industry Promotion Office, a Smart Machinery Development Center at Shuinan Smart City in Taichung, and a Smart Machinery Industrial Park at Fengzhou in Taichung City to assist construct up an ecosystem for the sensible equipment trade.
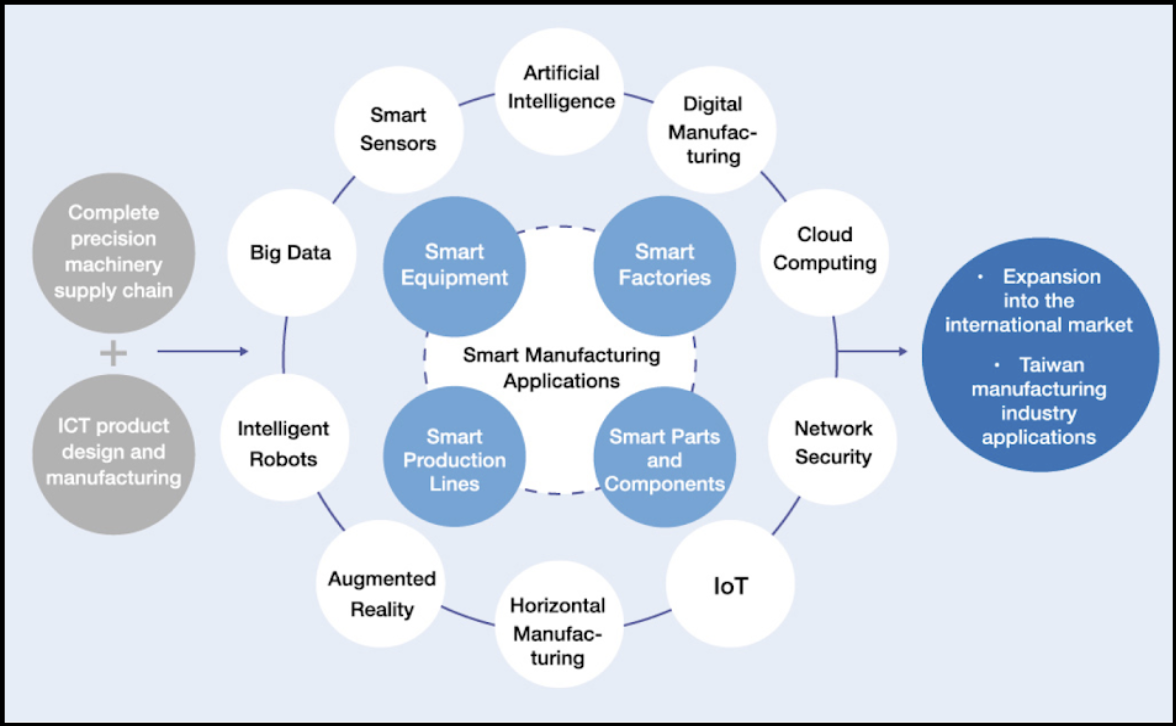
Image: A diagram depicting how Taiwan beneath the Tsai Administration deliberate to develop its sensible equipment trade as half of the Smart Machinery Development Plan. (Image Source: Taiwan MOEA)
The Six Core Strategic Industries
During Tsai’s second time period, the Executive Yuan launched the Six Core Strategic Industries—an initiative based on the 5+2 Industrial Innovation Plan. The initiative, launched on December 10, 2020, focused six industries: 1) digital expertise, 2) cybersecurity, 3) medical expertise and precision well being, 4) inexperienced and renewable power, 5) nationwide protection and strategic industries, and 6) strategic stockpile industries. Although the Six Core Strategic Industries initiative was launched within the wake of COVID-19 and towards the backdrop of a massively escalating commerce battle between the United States and China, it aimed to primarily handle the growing sophistication of cyber threats facing Taiwan and the shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals in Taiwan. This curiosity in cybersecurity was not new—Tsai had first articulated the precept that cybersecurity is inseparable from national security in 2019. This was emphasised once more in Tsai’s second inaugural speech of May 2020, when she acknowledged: “We are going to develop a cybersecurity industry that can integrate with 5G, digital transformation, and our national security. We will strive to create cybersecurity systems and an industrial chain that can protect our country and earn the world’s trust.” Thus, not like the 5+2 Industrial Innovation Plan, the following Six Core Strategic Industries targeted on enhancing Taiwan’s nationwide safety—notably by means of cybersecurity—somewhat than merely boosting technology-driven financial progress.
However, Taiwan nonetheless confronted challenges when it got here to expertise shortages. The National Science and Technology Development Plan (2021-2024) acknowledged that: “Taiwan still has a shortage of cybersecurity talent and there is still plenty of room for improvement in terms of R&D capacity to cybersecurity.” To assist the event of nationwide cybersecurity options in keeping with the Six Core Strategic Industries, the Ministry of Digital Affairs (MODA, 數位發展部) organized the CYBERSEC convention in May 2023—which was later repeated in 2024 and 2025. In 2024, Tsai stated that CYBERSEC 2024 would “promote exchanges and inspire more cooperation among the academic, public and private sectors from home and abroad to strengthen the global cybersecurity network.” According to MODA, CYBERSEC is the largest cybersecurity exhibition in the Asia-Pacific region, with 48 cybersecurity corporations showcasing their services on the 2023 convention. Overall, CYBERSEC was an effort by the Taiwanese authorities to facilitate regional cooperation and trade on cybersecurity points, whereas additionally attracting expertise throughout the Asia-Pacific area to Taiwan’s cybersecurity trade.
A New Era of Technological Development
A 2023 statement by the National Development Council (NDC, 國家發展委員會) lauded the success of the 5+2 Industrial Innovation Plan, noting that the annual income of a number of of the industries—together with the Internet of Things and biotechnology sectors—had surpassed NTD 1 trillion (USD 33 billion). This output underscores the success of Taiwan’s technological growth initiatives.
The Tsai Administration’s two flagship plans, the 5+2 Industrial Innovation Plan (2016) and the Six Core Strategic Industries (2020), harnessed superior expertise as a nationwide benefit in an effort to beat back financial slowdown. The plans sought to take Taiwan’s high-tech R&D international, assist human capital, wield trade 4.0 applied sciences, set up sensible equipment growth facilities, and promote cybersecurity. Capitalizing on non-public funding, the Tsai Administration launched a brand new period of development in Taiwan’s excessive expertise sectors.
However, Taiwan’s labor shortages weren’t solved by means of these two flagship plans and Tsai’s new period of technological growth was unsuccessful in rising new expertise within the high-tech industries. Despite her efforts in advancing worldwide prime expertise by means of the Asia Silicon Valley, the sensible equipment trade, and CYBERSEC, the number of those talents who are interested in coming to Taiwan remains small. The financial slowdown will under no circumstances be staved off except there’s a surge within the pool of expertise expertise. Accordingly, Lai’s Five Trusted Industry Sectors Promotion Plan ought to vastly prioritize labor shortages together with the worth of democracy.
The essential level: Former President Tsai Ing-wen got here into workplace in a interval of financial slowdown that had begun within the Nineties, main her to reshape Taiwan’s nationwide competitiveness utilizing superior applied sciences. Tsai outlined two vital plans: the 5+2 Industrial Innovation Plan and the Six Core Strategic Industries, which considerably emphasised human capital and the burgeoning cybersecurity sector. Still, future expertise insurance policies ought to proceed to prioritize labor shortages to counter an financial slowdown.
[1] On July 27, 2022, the Ministry of Science and Technology was reorganized as a ministry-level council named the National Science and Technology Council.
