Precise measurement of magnetic fields underpins many areas of science and expertise, and researchers regularly search extra delicate and sensible magnetometry strategies. Yuxiang Huang, Wei Wu, and Qingyuan Mei, from the (*13*) of Science and Technology of China, alongside Yiheng Lin, now current a promising advance in scalable radio-frequency magnetometry utilizing trapped ions. Their work demonstrates a technique that mixes established strategies with a novel method to suppressing noise and magnetic discipline variations, reaching a sensitivity that would considerably enhance current measurements. The group’s simulations reveal the potential to increase coherence occasions to a number of minutes, paving the way in which for sturdy and sensible magnetometry methods with broad purposes in fields starting from supplies science to basic physics.
Trapped Ions Detect Picotesla Magnetic Fields
Quantum magnetometry is a basic space of contemporary physics, with purposes spanning supplies science, biomedical imaging, and exams of basic physics. This work particulars an experimental method to constructing a scalable radio-frequency magnetometer utilizing trapped ions, aiming for top sensitivity and spatial decision. The magnetometer exploits the spin states of particular person ions, held and managed inside an electromagnetic lure, to detect weak radio-frequency magnetic fields. By exactly manipulating and measuring the ion’s spin resonance, the system guarantees to resolve magnetic discipline variations with unprecedented accuracy, doubtlessly reaching sensitivities exceeding 10 picotesla per root Hertz.
The method centres on using a series of individually addressable ions, every performing as a miniature magnetic sensor, and utilising radio-frequency fields to drive transitions between their spin states. The ions are cooled to their lowest power state to minimise disturbances and improve measurement precision, and their spin states are initialised and skim out utilizing laser-induced fluorescence. A key innovation lies within the improvement of a multiplexed readout scheme, permitting simultaneous detection of magnetic fields at a number of spatial places, considerably rising the magnetometer’s efficient sensing space and scalability. This analysis introduces a novel structure for a scalable quantum magnetometer, overcoming limitations of single-sensor designs, and providing a pathway in direction of high-resolution, three-dimensional magnetic imaging.
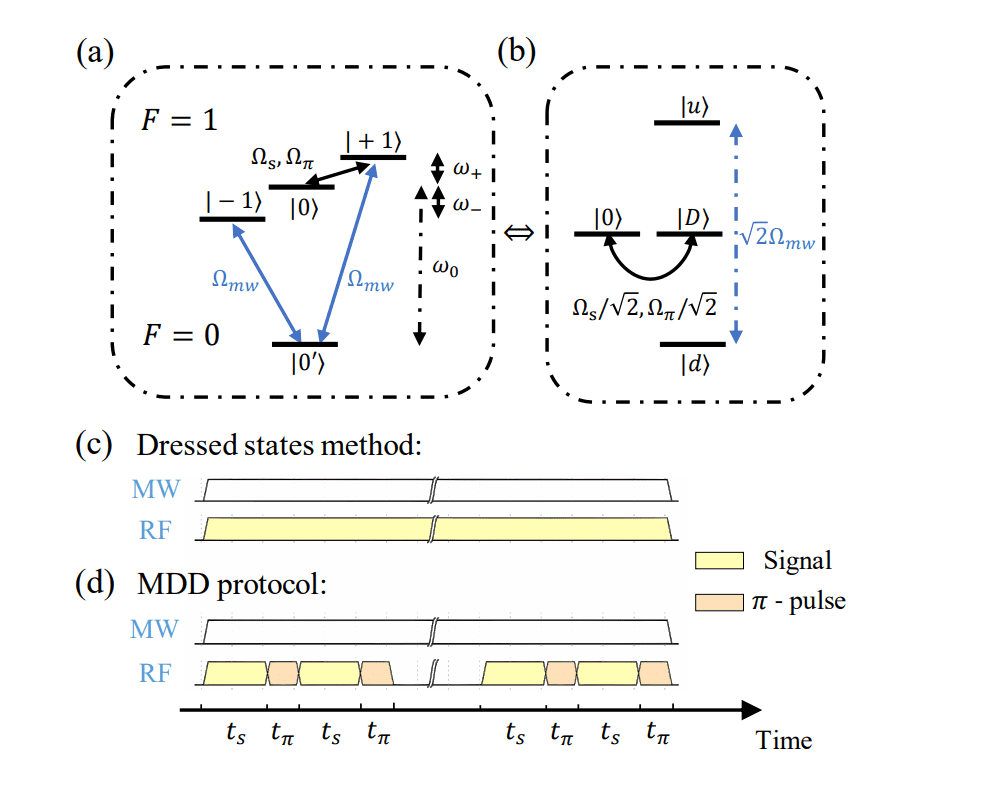
With its potential for parallel readout and enhanced sensitivity, the proposed system guarantees to advance quantum sensing, enabling new investigations into a variety of scientific and technological challenges, together with the detection of weak biomagnetic alerts and the characterisation of nanoscale magnetic supplies. Furthermore, the demonstrated scalability represents a vital step in direction of constructing sensible, large-scale quantum sensors for real-world purposes. A key part of quantum metrology entails trapped-ion methods, which have achieved picotesla per root Hertz sensitivity in single-ion radio-frequency magnetic discipline measurements by way of dressed states and dynamical decoupling. This work proposes a scalable trapped-ion magnetometer utilising a blended dynamical decoupling technique, combining dressed states with periodic sequences to suppress disturbances and spatial magnetic discipline inhomogeneity.
The technique entails fastidiously engineered radio-frequency pulses utilized to the ions, making a superposition of quantum states delicate to exterior magnetic fields. By combining the strengths of each dressed states and periodic decoupling sequences, the magnetometer goals to enhance sensitivity and scalability in comparison with current approaches. This method successfully mitigates the consequences of environmental noise and imperfections within the magnetic discipline, enabling extra exact measurements over bigger volumes. Trapped ions, held in place utilizing electromagnetic fields, enable for exact management and isolation of particular person ions or giant crystals of ions.
Quantum metrology utilises quantum phenomena, corresponding to superposition and entanglement, to boost the precision of measurements past classical limits. Mixed dynamical decoupling is a way to guard qubits from environmental noise, essential for sustaining coherence and bettering sensor sensitivity. Ions organize themselves into ordered buildings as a consequence of electrostatic repulsion, offering a secure atmosphere for quantum operations. Micromotion, a residual oscillatory movement of the ions throughout the lure, might be harnessed for improved management. Sympathetic cooling cools ions of 1 species by coupling them to a different, colder species, reaching very low temperatures important for decreasing noise and bettering coherence.
Optical clocks utilise the exact frequencies of optical transitions in ions to create extremely correct clocks, whereas microwave clocks utilise microwave transitions. The group can be growing sensors based mostly on trapped ions to detect weak magnetic fields, doubtlessly for purposes in magnetoencephalography and magnetomyography, which detect mind and muscle exercise with excessive spatial and temporal decision, and for basic physics analysis. Extending the time for which qubits preserve their quantum state is a serious problem, and this analysis explores strategies like blended dynamical decoupling and cautious lure design to minimise disturbances. The group reviews reaching coherence occasions exceeding one hour in some instances.
Increasing the variety of qubits in a trapped ion system is essential for constructing extra highly effective sensors and quantum computer systems, and this analysis addresses challenges associated to controlling and entangling giant numbers of ions. The group can be investigating methods to mitigate or exploit micromotion to enhance the efficiency of trapped ion methods, and utilizing molecular dynamics simulations to grasp and optimise the behaviour of trapped ion crystals. The analysis has reported coherence occasions exceeding one hour for single ion qubits, and the event of clocks with fractional frequency stability approaching 10^-18. High-fidelity quantum gates have been demonstrated utilizing trapped ions, and the efficient use of blended dynamical decoupling to guard qubits from noise.
Precise measurement of hyperfine splitting in cadmium ions, essential for clock improvement, has additionally been achieved, together with profitable cooling of ions utilizing sympathetic cooling strategies. These developments have potential purposes in superior timekeeping, biomedical imaging, basic physics analysis, quantum computing, and geophysics. This analysis demonstrates a scalable trapped-ion magnetometer able to extremely delicate radio-frequency magnetic discipline measurements. By combining dressed states with a blended dynamical decoupling technique, scientists achieved prolonged coherence occasions and sturdy resilience in opposition to magnetic discipline drift and spatial inhomogeneity.
Numerical simulations, utilising practical experimental parameters, point out a sensitivity of 13 for radio-frequency discipline detection, representing a big development in magnetometer expertise. The group efficiently demonstrated improved sensitivity in each single-ion and bigger, scalable methods containing as much as 10,000 ions. Notably, the blended dynamical decoupling technique achieved a sensitivity of 13 fT/√Hz within the scalable system, highlighting its potential for sensible purposes. Beyond enhanced sensitivity, the massive spatial extent of the ion crystal presents a singular functionality for probing magnetic discipline gradients by partitioning the crystal or resolving alerts from distinct areas.
This work establishes a robust basis for future developments in magnetometry and will profit numerous fields, together with the seek for interactions between spins and darkish matter, and the advance of coherence in different quantum methods, corresponding to rare-earth ions and impartial atom arrays. The authors acknowledge that coherence occasions are barely diminished in bigger methods, an element that will probably be addressed in future work. Further analysis will give attention to optimising the tactic for even higher sensitivity and exploring its software to extra advanced magnetic discipline environments.