Exploratory spatial information evaluation (ESDA)
Exploratory spatial information evaluation is an important analysis space in spatial econometrics, exploring spatial dependence and correlation related to spatial location. This paper goals to guage the spatial distribution patterns of STFE and city TFCP by utilizing exploratory spatial information evaluation, and we employed the worldwide Moran’s I index for spatial correlation assessments.
Temporal variation traits of TFCP and STFE
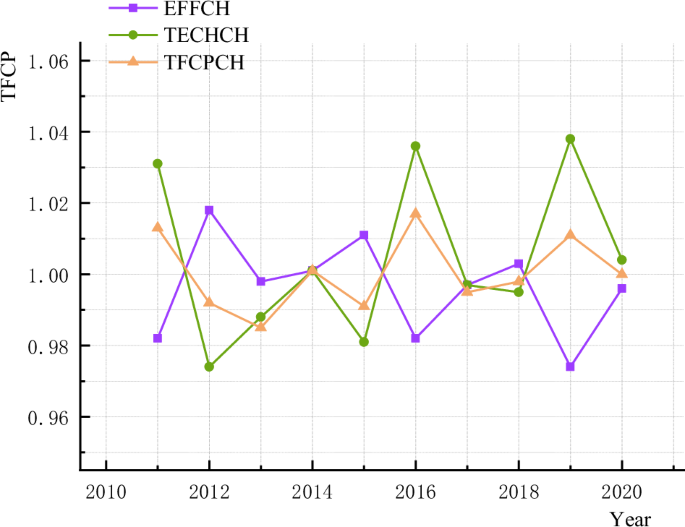
A line chart is used to reveal the altering development within the common worth of TFCP throughout 284 prefecture-level municipalities from 2011 to 2020. Figure 2 illustrates the development in whole issue carbon productiveness (TFCHCH) and its decomposition objects, technological progress (TECHCH) and technological effectivity (EFFCH). From 2011 to 2020, the TFCP demonstrated a gradual fluctuation across the worth of 1, exhibiting a “W” formed development with minimal and most factors in 2013 and 2016, respectively. Moreover, the development in technological progress has all the time been in step with TFCP, and it’s extra unstable than TFCP. Conversely, technological effectivity and TFCP comply with virtually contrasting developments, suggesting that technological progress is the first driver for selling TFCP.
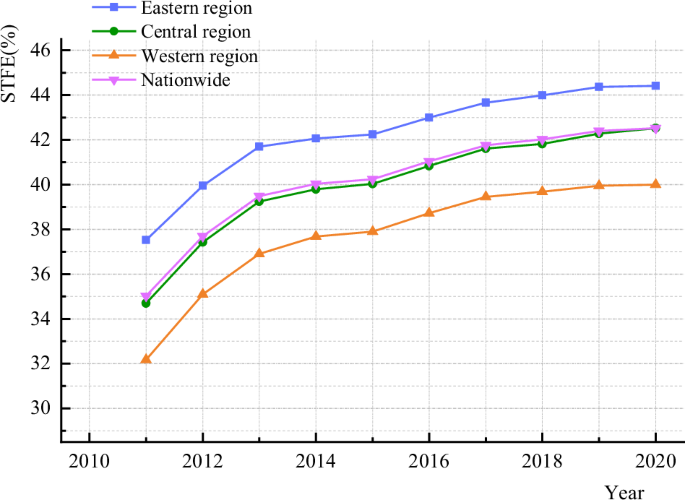
As illustrated in Fig. 3, the typical degree of STFE in each the nation as an entire and its subregions confirmed a constant upward development between 2011 and 2020. In phrases of regional variation, the development is “east > central > west”. Notably, the jap area’s STFE degree surpasses the nationwide common, on account of its standing as a major hub for China’s financial participation within the world financial system. The area boasts absolutely practical financial establishments, ample financial assets, unimpeded financing channels, and in depth information sharing, and performs an more and more distinguished function in driving scientific and technological innovation and growth.
Spatial distribution patterns of TFCP and STFE
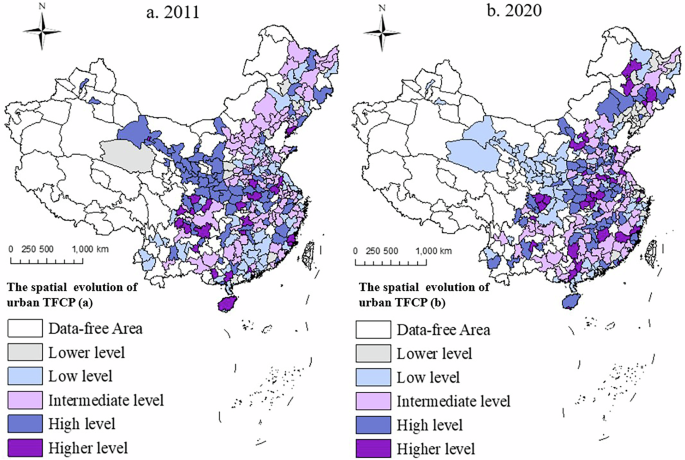
Figure 4 illustrates the spatial evolution patterns of TFCP throughout prefecture-level cities in 2011 and 2020. It may be noticed that in 2011–2020, cities with low and very low TFCP accounted for greater than 50% of all cities, these with medium TFCP constituted 40% of the pattern, and the remaining had been cities with comparatively excessive and excessive TFCP ranges. Generally, there’s a spatial distribution sample of TFCP characterised by the predominance of blocky distribution in center and low-level cities, complemented by level distribution in high-level cities. This spatial distribution sample continued considerably unchanged for a span of 10 years, exemplifying the traits of a sturdy spatial construction.
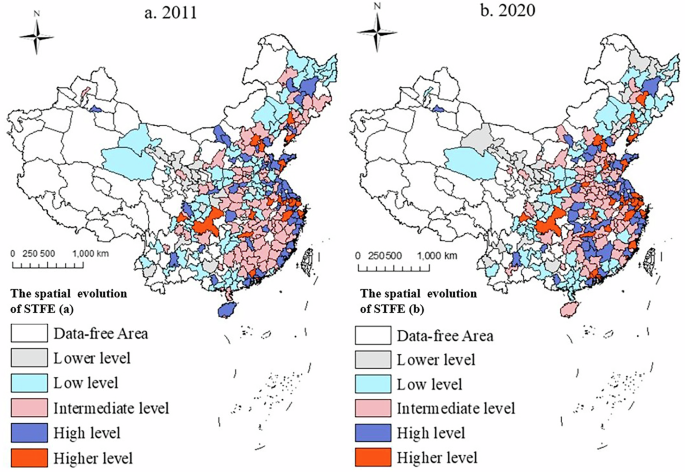
This examine additionally drawn a spatial visualization map of the STFE (Fig. 5). Comparing the maps of 2011 and 2020, it’s evident that the darkish blue and purple zones have elevated considerably, indicating an total rising development within the degree of China’s STFE, and there’s important spatial heterogeneity.
Regionally, the STFE within the jap area is considerably greater than that within the central and western areas, presenting a attribute of “high in the east and low in the west”, which is in step with the development of China’s financial growth (Zhao et al., 2022a). Among them, the southeast coastal cities and city agglomeration of the Yangtze River Delta have greater STFE ranges than different areas. With the rising richness of technology finance entities, the continual optimization of the STFE setting, and the gathering of high-level scientific and financial abilities, the STFE in these areas is at a better degree. Hunan, Hubei, and Henan provinces within the central area have developed STFE to a sure extent with the backing of the technique of the rise of central China. Apart from Sichuan province and Chongqing metropolis, STFE ranges in different areas are low. This could also be on account of the truth that the western area has not but developed a sound technology financial service system, which is in step with Shen et al.’ (2023) perspective.
Spatial correlation evaluation
As illustrated in Table 1, the worldwide Moran’sIindex distinctly registered as positively important on the 1% degree beneath the three weight matrices of geographic distance (({W}_{1})), financial distance (({W}_{2})), and geographic and financial nested distance (({W}_{3})). This urged that China’s TFCP reveals a constructive spatial correlation from 2011 to 2020, revealing a bent in the direction of spatial aggregation. This implies areas surrounded by areas with excessive TFCP sometimes have comparatively elevated TFCP.
Regression outcomes evaluation of DSDM
To decide whether or not to make use of a fixed-effects mannequin or a random-effects mannequin, the Hausman check yielded a statistic of 60.31 with a p worth of 0.0000, indicating that the fixed-effects mannequin needs to be used. Therefore, the DSDM mannequin with bidirectional fastened impact was recognized as optimum.
In distinction to the spatial lag and error fashions, the SDM comprehensively considers the spatial correlation of each the explanatory and defined variables. To take note of the dynamics and lags of TFCP and keep away from potential endogeneity points that may bias estimation outcomes, a DSDM was constructed to discover the impression of STFE on TFCP based mostly on related literature (Zhao et al., 2022b).
$$start{array}{l}{{TFCP}}_{{it}}={beta }_{0}+{beta }_{1}{{TFCP}}_{i,t-1}+{beta }_{2}{{STFE}}_{{it}}+{beta }_{3}{X}_{{it}}+{rho }_{1}mathop{sum }limits_{i=1}^{n}W{{TFCP}}_{{it}}qquadqquad;,+,{rho }_{2}mathop{sum }limits_{i=1}^{n}W{{TFCP}}_{i,t-1}+{rho }_{3}mathop{sum }limits_{i=1}^{n}W{{STFE}}_{{it}}qquadqquad;,+,{rho }_{4}mathop{sum }limits_{i=1}^{n}W{X}_{{it}}+{mu }_{i}+{v}_{t}+{varepsilon }_{{it}}finish{array}$$
(22)
the place ({{TFCP}}_{{it}}) represents whole issue carbon productiveness; ({{TFCP}}_{i,{t}-1}) represents the lagged interval of whole issue carbon productiveness; ({{STFE}}_{{it}}) stands for science and technology financial ecology; ({X}_{{it}}) denotes the management variable; (W) represents the spatial weight matrix; (rho) represents the spatial impact coefficient; ({mu }_{i}) denotes metropolis fastened impact; ({v}_{t}) denotes the time fastened impact; ({varepsilon }_{{it}}) denotes a random error time period.
Table 2 presents the influences of STFE on TFCP beneath totally different weight matrices. The findings of the static SDM are introduced in columns 1, 3, and 5, whereas these of the DSDM are in columns 2, 4, and 6. It is observable that the coefficients of the lagged TFCP are considerably constructive within the financial distance matrix and the economic-geographical nested matrix, denoting the persistence of TFCP inside these two matrices. The coefficients of the spatially lagged TFCP are considerably constructive on the 1% degree solely within the financial matrix, indicating that the TFCP reveals important spatial spillover effects and spatial-dimension synergistic correlation within the financial distance matrix. Compared with the geographical channel, the advance of TFCP on this area has a sure “demonstration effect” on neighboring areas by means of the financial channel, facilitating the advance of TFCP in these areas.
For the core explanatory variables, the coefficients of STFE show notable positivity beneath each static and dynamic SDM, suggesting that STFE’s affect on TFCP possesses a considerable spatial enhancement impact. By evaluating the coefficient values for columns 2, 4, and 6, it’s discovered that this impression primarily diffuses by means of financial channels. Furthermore, the coefficient of spatial lag time period in STFE reveals appreciable negativity beneath the three weight matrices, implying that the enhancement of STFE could procure the assets of adjoining areas and probably generate antagonistic externalities of “beggar-thy-neighbor”. The fast growth of native STFE can appeal to high-end labor and assets, reminiscent of financial and scientific personnel, from neighboring areas. This can result in the loss of expertise and assets from these areas and hinder the event of neighboring STFE.
The outcomes of the direct impact present that, for each the static SDM mannequin and the dynamic SDM mannequin, the coefficient values of the STFE are considerably constructive. This signifies that the native STFE can promote native city carbon emission reduction, thus verifying Hypothesis 1. For each the static and dynamic SDM fashions, the coefficients of the oblique effects of the STFE are considerably adverse on the 1% degree. This signifies that native growth of an STFE has a adverse impression on carbon emission reduction in neighboring cities, particularly producing a adverse spatial spillover impact, which validates Hypothesis 2.
The potential causes for this example are as follows. Firstly, there’s useful resource competitors and siphoning impact. In phrases of financial assets, native areas with well-developed science and technology finance have a tendency to draw extra financial establishment investments and capital inflows, and native STFE growth could result in intense useful resource competitors. Regarding expertise assets, a high-quality native STFE affords extra growth alternatives and excessive salaries, attracting expertise from neighboring areas. Neighboring cities, on account of expertise loss, have decreased scientific and technological R&D and innovation capabilities and are underdeveloped in new applied sciences and modes for selling carbon emission reduction. This useful resource siphoning impact undermines the useful resource base of neighboring cities’ carbon emission reduction efforts and is unfavorable to their carbon emission reduction course of. Secondly, it could be attributable to regional obstacles to technological innovation. There could also be regional diffusion obstacles to technological improvements pushed by the native STFE. Low-carbon applied sciences developed by native enterprises and analysis establishments with the help of science and technology finance could also be onerous to be promoted and utilized in neighboring cities as a result of of extreme mental property rights safety and company aggressive methods.
Robustness and endogenous assessments
Replaced the defined variable
This examine recalculated the TFCP beneath the financial distance weight matrix, utilizing the formulation beneath that primarily expresses the ratio of every metropolis’s GDP to its carbon dioxide emissions. As revealed inside the column 1 of Table 3, the coefficients and significance had been in alignment with the benchmark regression outcomes, signifying that the conclusions had been dependable.
$${{RETFCP}}_{{it}}={{GDP}}_{{it}}/{left({{CO}}_{2}proper)}_{{it}}$$
(23)
Replaced spatial weight matrix
The inverse geographic weight matrix was utilized to interchange the unique spatial matrices. The distance between any two cities is calculated based mostly on their longitude and latitude, and the reciprocal is taken. The farther the space between the 2 locations, the much less the flexibility to affect one another. The ends in column 2 of Table 3 present principally constant coefficients and significance with the benchmark regression, signifying strong conclusions from this paper.
Replacement of the indicator weighting methodology
Calculating the weights of the indications by means of the coefficient of variation methodology could rely an excessive amount of on the target information efficiency, thus leading to dynamic modifications within the weighting outcomes because the pattern varies. Therefore, this paper additional adopts the equal weight methodology and principal part evaluation methodology to calculate the STFE growth degree and conducts the robustness check. Among them, the equal weight methodology signifies that every first-level indicator has the identical weight, and its subordinate second-level indicators are additionally assigned values with the identical weight. As may be seen from the ends in columns 3 and 4 of Table 3, altering the burden calculation methodology doesn’t have an effect on the empirical outcomes, which stay in step with the benchmark regression.
Endogenous check
Although the theoretical evaluation signifies that the event of the STFE is one of the elements influencing carbon emission reduction, there nonetheless exists an endogeneity downside attributable to reverse causality. To handle the endogeneity concern ensuing from reverse causality between the explanatory variables and the defined variable, this paper, drawing on the analysis of Jin (2019), re-estimates the parameters of the benchmark regression equation utilizing the Generalized Spatial Two-Stage Least Squares (GS2SLS) methodology. This strategy doesn’t require the unbiased choice of exterior instrumental variables. Instead, it solely must generate instrumental variables by using the spatial lag phrases and numerous explanatory variables for a sturdy estimation, which might successfully cut back the bias within the estimation outcomes attributable to the endogeneity downside. Table 4 studies the parameter estimation outcomes of GS2SLS. Firstly, the F-statistics within the first stage beneath the settings of the three weight matrices are all >10. Therefore, there isn’t any want to fret about the issue of weak instrumental variables. Secondly, as may be seen from the parameter regression outcomes, after taking the endogeneity downside into consideration, the STFE nonetheless reveals a major carbon emission reduction impact, which verifies the robustness of the conclusions of this paper.
Heterogeneity evaluation
Regional heterogeneity
Due to variations in useful resource endowments, innovation bases, and ranges of financial growth throughout totally different areas in China, there could also be disparities within the effectiveness of selling regional STFE to boost TFCP. Therefore, this part goals to additional analyze regional heterogeneity impacts beneath the financial weight matrix.
Columns 1–3 of Table 5 current the outcomes of regional heterogeneity within the impression of STFE on the spatial spillover effects of TFCP. For the direct impact outcomes, solely the STFE coefficient within the jap area is considerably constructive on the 1% degree, whereas the STFE coefficients within the central and western areas aren’t important. This signifies that among the many three main areas, solely the native STFE growth within the jap area has a major carbon emission reduction impact. For the oblique impact outcomes, among the many three main areas, solely the STFE coefficient within the jap area is considerably adverse on the 1% degree, whereas these within the central and western areas are adverse however not important. This means that the event of STFE within the jap area has a adverse impression on carbon emission reduction in surrounding areas, that’s, it generates a adverse spatial spillover impact.
The potential cause is that the jap area undergoes sooner industrial upgrading in the course of the growth of STFE (Chen et al., 2024). Due to the commercial gradient distinction between the east and the central and western areas, some high-carbon industries within the east will likely be transferred to the central and western areas in the course of the industrial construction optimization course of. Such industrial switch typically lacks efficient low-carbonization constraints and steering mechanisms. When the central and western areas obtain these industries, they could face difficulties in greening them as a result of of their very own restricted technical degree and capital, thereby rising native carbon emissions and impeding the advance of carbon emission reduction. Moreover, this industrial switch could disrupt the unique industrial ecological stability within the central and western areas and hinder the event of low-carbon industries that initially had growth potential.
Resource endowment heterogeneity
Compared with non-resource-based cities that rely on rising industries, resource-based cities usually rely extra on the event and processing of native pure assets. Therefore, the exploitation and utilization of considerable pure assets in resource-based cities could result in greater carbon emissions. In this examine, pattern cities had been divided into two teams (resource-based cities and non-resource-based cities) for heterogeneous comparative evaluation by referring to the listing of resource-based cities specified within the “National Sustainable Development Plan for Resource-Based Cities (2013–2020)”. The particular outcomes are introduced in Columns 4–5 of Table 5.
The outcomes of direct effects present that the coefficient of STFE is considerably constructive on the 5% degree solely in non-resource-based cities, indicating that the carbon emission reduction impact of the STFE is extra pronounced in non-resource-based cities in comparison with resource-based cities. The outcomes of oblique effects reveal that the coefficient of the STFE is considerably constructive on the 5% degree solely in non-resource-based cities. This means that the promotion impact of native STFE growth on carbon emission reduction in neighboring areas is extra important in non-resource-based cities than in resource-based cities, that means that the spatial spillover impact of the carbon emission reduction impact of the STFE is extra evident in non-resource-based cities.
The potential cause is that useful resource cities often have a unitary industrial construction with useful resource extraction and processing because the dominant business. In distinction, non-resource cities possess a extra diversified industrial construction (Li et al., 2024), incorporating manufacturing, service, and high-tech industries. These industries have a better demand for scientific and technological innovation, and the STFE can supply them extra growth alternatives. Technical exchanges and cooperation amongst non-resource cities are additionally extra frequent, which facilitates the fast dissemination and spillover of low-carbon applied sciences.
With the adjustment and upgrading of the commercial construction of non-resource cities, some extremely polluting and energy-consuming industries could also be relocated to different areas. In this course of, the STFE can information the business switch in a low-carbon course, stopping the disorderly switch of polluting and high-carbon-emission industries amongst totally different areas. Such business switch can promote the synergistic growth of industries between areas, improve the effectivity of useful resource utilization, cut back carbon emissions, and improve TFCP.
Heterogeneity of financial growth degree
Regional variations within the degree of financial growth could have an effect on the carbon reduction effects of STFE. The ratio of financial establishments’ mortgage balances to GDP on the finish of the 12 months was used to assemble the index of financial growth degree on this examine. Based on the imply worth of the financial growth degree, all samples had been categorised as excessive financial growth degree group and low financial growth degree group, then regressed sequentially. Regression outcomes are proven in columns 6 and 7 of Table 5.
By evaluating columns 6 and 7, it may be seen that in areas with a excessive degree of financial growth, the coefficient values of STFE are considerably constructive on the 5% degree for each direct and oblique effects. This implies that the event of STFE in these areas considerably contributes to carbon emission reduction each regionally and in neighboring areas. However, in areas with a low degree of financial growth, these two coefficients aren’t important, indicating that the event of STFE in these areas makes no important contribution to carbon emission reduction both regionally or in neighboring areas.
The degree of financial growth is essential for selling the carbon emission reduction impact of the STFE. When the financial growth degree is greater, extra funds will likely be allotted to inexperienced enterprises, and the inhibitory impact on the carbon emission conduct of closely polluting enterprises will likely be extra apparent, which helps to boost the TFCP. However, when the financial growth degree is low, the regional financial system is much less full, and the implementation effectivity of financial insurance policies will lower. The financial system could not have the ability to execute the provisions within the STFE, failing to moderately allocate funds from closely polluting enterprises to inexperienced enterprises, and thus being unable to successfully restrain the pollutant emission behaviors of closely polluting enterprises. As a consequence, carbon emissions improve, and the enhancement of TFCP is inhibited.
Mechanisms evaluation
The check outcomes of the moderating impact are proven in Table 6. The outcomes of columns 1–4 point out that the event of STFE has considerably promoted the advance of inexperienced technology innovation, informatization degree, human capital degree, and the effectivity degree of financial useful resource allocation. Columns 5–8 report the check outcomes of the interplay between STFE and the moderating variables. It may be seen that the interplay phrases of STFE with inexperienced technology innovation, STFE with the informatization degree, and STFE with the human capital degree are all considerably constructive on the 5% degree. This signifies that the event of STFE has strengthened the emission reduction effects of inexperienced technology innovation, informatization degree, and human capital degree on native city carbon emissions. However, the moderating impact of the effectivity of financial useful resource allocation on the impression of native carbon emission reduction shouldn’t be important.
Possible explanations are as follows. For inexperienced technology innovation, the STFE affords financial help, reducing innovation prices for enterprises. This permits them to speculate extra in inexperienced R&D, selling emission-reduction tech breakthroughs and purposes. In phrases of informatization, a better-developed ecosystem boosts data move. Enterprises can entry low-carbon tech information sooner, modify manufacturing methods, and optimize processes to chop waste and emissions. As for human capital, the ecosystem channels funds into training and coaching. More modern abilities are cultivated, who can drive inexperienced tech progress and implement low-carbon methods in enterprises, thus decreasing native city emissions.
Columns 5–8 additionally report the spatial effects of the interplay phrases between STFE and the moderating variables. The spatial phrases of the interplay between STFE and the 4 moderating variables are all considerably adverse. This signifies that the event of STFE, by means of inexperienced technology innovation, informatization degree, human capital degree, and the effectivity of financial useful resource allocation, promotes the rise in carbon emissions in neighboring areas, exacerbating the “beggar-thy-neighbor” adverse externality spatial impression of STFE, which verifies Hypothesis 2a. In distinction, the moderating mechanisms of the informatization degree and human capital degree exacerbate the adverse spatial externality of STFE’s impression on carbon emission reduction to a higher extent.
The potential explanations are as follows. In the facet of inexperienced technology innovation, the event of STFE allows native enterprises to safe extra funds for analysis and growth. Since the R&D achievements are preferentially utilized regionally, neighboring areas are put at a aggressive drawback. This could impel them to resort to high-carbon applied sciences to maintain manufacturing, thereby resulting in a rise in carbon emissions. At the extent of informatization, the event of STFE empowers native enterprises to entry data extra effectively. While optimizing their very own manufacturing processes, native enterprises depart neighboring areas lagging in data acquisition. As a consequence, the commercial adjustment in neighboring areas is sluggish, and the proportion of high-carbon industries comparatively will increase, inflicting an increase in carbon emissions. Regarding the human capital degree, the event of STFE attracts expertise to move into the native space. This results in a expertise drain in neighboring areas, leaving them brief of the mental help important for low-carbon transformation. Consequently, it turns into tough to cut back the carbon emissions of industries in these areas. In phrases of the effectivity of financial useful resource allocation, the event of STFE allows a extra rational allocation of native financial assets, which promotes the event of native industries. However, neighboring areas face difficulties in acquiring funds and could should rely on conventional high-carbon industries, thus leading to a rise in carbon emissions.
Limitation
Some limitations needs to be taken into consideration for a extra complete examine. First, in regards to the quantification of STFE metrics, further metrics may be included within the STFE metric system sooner or later, for instance, authorities establishments and science and technology corporations, to ensure that the quantification of STFE metrics is extra complete. Second, future analysis can discover the environmental implications of STFE from numerous views, reminiscent of a examine on the impacts of STFE on air pollution mitigation and carbon reduction. Third, with the accelerated growth of science and technology finance, the pattern scope may be expanded to an extended time dimension to additional examine the financial and environmental implications of STFE, making certain that the examine’s findings are extra convincing.