Astronomers have mapped in particulars the invisible layers of cosmic mud that veils our Milky Way and reddens the gentle of the stars. This might assist hint the areas the place subsequent technology of stars could also be forming.
Our galaxy, the Milky Way, is crammed with huge clouds of interstellar mud and fuel that may block or dim the gentle from stars. This is known as as ‘extinction’ of star gentle. Understanding how the mud is unfold throughout the Galaxy helps scientists be taught extra about the place stars kind and the construction of the Milky Way.
Scientists from Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES), an autonomous institute beneath the Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, used the knowledge from greater than 6,000 open clusters (a sort of star clusters), to chart the distribution of this interstellar mud throughout the Milky Way’s galactic airplane or disk. Most of these clusters lie near the Galactic disk which is the skinny airplane of the Galaxy the place interstellar matter is predominantly concentrated and star formation takes place. Therefore, they act as dependable tracers for mapping the distribution of interstellar mud, which absorbs and dims their gentle.
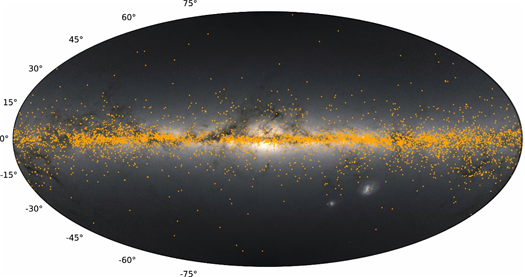
Fig: An on-sky view of Milky Way in the Galactic longitude-latitude (l-b) airplane generated by ESA Gaia Early Data Release 3 (EDR3) juxtaposed with the pattern of 6,215 Open Clusters (yellow dots) used on this examine. Most of the clusters are positioned in the Galactic mid-plane b = 0°
The examine led by Dr. Y. C. Joshi reveals that the mud just isn’t evenly distributed. Instead, it types a skinny, wavy layer that doesn’t align completely with the central airplane of the Galaxy, however relatively lies under it. This “reddening plane,” as scientists name it, shifts up and down in a wave-like sample as one appears to be like round the Galaxy. Most of the mud is present in the course of Galactic longitude 41°, whereas the least is round 221°. Interestingly, the Sun is positioned about 50 light-years (or roughly 15.7 parsecs) above this dusty layer.
The thickness of the mud layer additionally varies, being denser in some areas, particularly towards the Galactic heart, and thinner in others. This uneven distribution factors to the dynamic and sophisticated nature of our Galaxy’s construction. This mapping offers astronomers a clearer image of how mud is organized in our half of the Galaxy, which is essential for precisely learning stars and different galaxies. It additionally confirms that a lot of the mud is packed right into a slender band the place new stars are actively forming.
The examine highlights the want for future observations, particularly of extra distant areas, to construct an much more full three-dimensional view of the Milky Way’s dusty construction. Upcoming missions like Gaia’s subsequent knowledge launch and the Vera C. Rubin Observatory’s Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) will play a key function on this effort.
Publication hyperlink: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.newast.2025.102425
For extra particulars, please contact Dr. Yogesh C. Joshi (yogesh[at]aries[dot]res[dot]in)