The subsequent common expertise because the smartphone is on the horizon — and it could be rather less pocket pleasant.
The Moonshot analysis program, funded by the Japan Science and Technology Agency and accelerated by NVIDIA AI and robotics applied sciences, is working to create a world by 2050 the place AI-powered, autonomously studying robots are built-in into Japanese residents’ on a regular basis lives.
That’s simply goal No. 3 of the broader Moonshot initiative, which incorporates researchers from throughout Japan’s universities and contains 10 bold expertise targets — from ultra-early illness prediction to sustainable useful resource circulation.
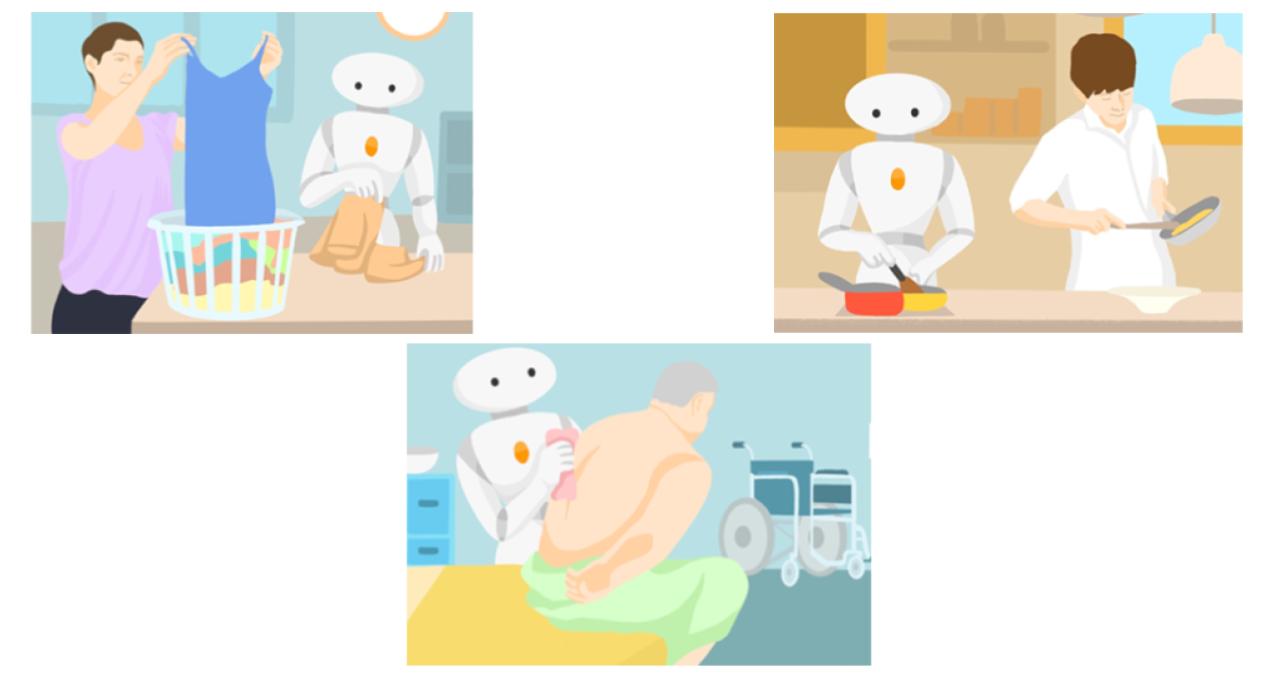
In gentle of Japan’s rising aged inhabitants, lots of the analysis initiatives underway heart on how robots can assist in senior care. This contains designing a robotic that’s able to caregiving duties like cooking, cleansing and hygiene care.
NVIDIA Architecture Powers On Moonshot Robots
NVIDIA applied sciences are built-in into each stage of the Moonshot mission’s senior care robots generally known as AI-Driven Robot for Embrace and Care, or AIREC.
Dry-AIREC robotic, the bigger and extra cell member of the Moonshot household, has two NVIDIA GPUs onboard. For AIREC-Basic, primarily used for knowledge assortment for the movement basis mannequin, three NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX modules energy AI processing on the edge.
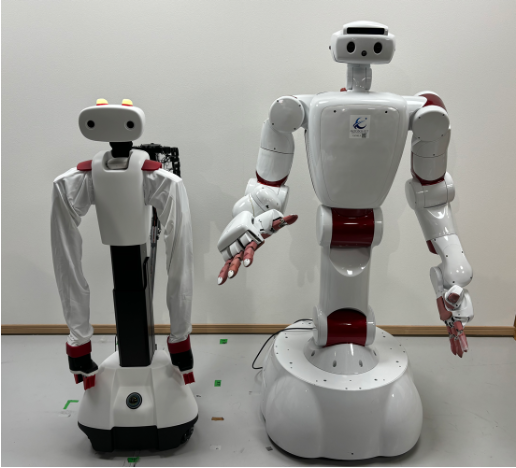

Plus, NVIDIA Isaac Sim, an open-source robotic simulation framework, was used to coach the AIREC robots to carry out particular duties, comparable to estimating the forces between objects.
The integration of NVIDIA applied sciences and AI into the robotic improvement course of has allowed this mission to go from a far-fetched dream to actuality quicker than imagined.
“Five years ago, before generative AI, few people believed that this application was possible,” mentioned Tetsuya Ogata, professor and director of the Institute for AI and Robotics at Waseda University. “Now, the atmosphere surrounding this technology has changed, so we can seriously think about this kind of application.”
Building a Full Set of Caregiving Capabilities
Additional analysis initiatives are underway to develop the Moonshot robotic’s elderly-care capabilities.
“We’re focusing on things like changing diapers, helping patients take baths and providing meal assistance, so those actions can be supported by the robots, and caregivers can focus on improving the patients’ lives,” mentioned Misa Matsumura, a bioengineering grasp’s scholar on the University of Tokyo.
A current paper by Matsumura — offered on the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems — targeted on repositioning, a necessary motion in aged care to stop mattress sores and allow diaper altering.
Automating repositioning with a humanoid robot — whereas contemplating the aged care sufferers’ private states and bodily wants — isn’t any straightforward feat.
To practice the Dry-AIREC robots for this analysis endeavor, Matsumura’s staff used laptops powered by NVIDIA RTX GPUs.
Matsumura used 3D posture estimation, trajectory calculations and power estimation to additional develop the robots’ capabilities.
Dry-AIREC’s fisheye and depth cameras helped assess the actions required to reposition sufferers. The actual repositioning methodology wanted for a affected person is discovered by trajectory calculations primarily based on motion knowledge from expert caregivers.
The robotic should additionally use the correct amount of power in repositioning to finish the motion with out inflicting the affected person ache. By predicting the strain required to press the shoulders and knees, it determines the suitable timing for motion — enabling actions with the best utilized power.
Preliminary experiments had been finished utilizing mannequins, and Matsumura’s analysis has now superior to include people testing the robots. Matsumura is conducting ongoing analysis to additional enhance this motion for Dry-AIREC.
Among the various initiatives inside the Moonshot program, creating robots for aged care has specific significance for a few of the researchers as a result of mission’s social and private implications.
“Although my study focus is on medical robotics, I decided to join this project because my mother is growing older, and that experience has given me an appreciation for the importance of personal care,” mentioned Etsuko Kobayashi, professor of bioengineering on the University of Tokyo and Matsumura’s graduate advisor. “I found that my experience in medical robotics can be meaningfully extended to care robotics, contributing to the development of safe and reliable robotic systems for human-centered applications.”
The Moonshot staff for purpose No. 3 will showcase their progress on the 2026 International Symposium on System Integration in January.
Learn extra about NVIDIA Isaac Sim.