Significant time lags usually exist between scientific discoveries and technological improvements, typically spanning a few years earlier than manifesting into new applied sciences (Shibata et al., 2010; Hsiao and Torvik, 2019; Ba et al., 2024). In a seminal research, Globe et al. (1973) noticed that cutting-edge improvements with profound social impacts might be propelled by S&T interactions. Subsequently, students delved into elucidating the S&T nexus and technological innovation to understand innovation processes (Lee et al., 2018; Li et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2023; Zhao et al., 2023). The dynamics of S&T interplay represent an intricate course of involving the efficacy of S&T programs in remodeling present information paradigms, the effectivity of transformation, and spatial and temporal impacts on transformation tempo (Li et al., 2021; Yu et al., 2024). Scientific information programs symbolize advanced networks of interconnected ideas, with “associationism” adapting these ideas to real-world functions over time (Plotkin, 1997). These information programs, amalgamating pure and social sciences, endeavor to assemble hierarchical principle/mannequin buildings (Fuchs, 1986; Kim et al., 2024). Conversely, technical information programs exhibit a extra pragmatic orientation, primarily targeted on the software and processing of info into improvements addressing technical and enterprise challenges inside companies or industries (Amadi-Echendu, 2007; Shibata et al., 2010; Ba et al., 2024). Initially, scientific information could circuitously affect technological innovation inside companies, because it doesn’t inherently emerge to resolve technical or enterprise points (Gittelman and Kogut, 2003). Nonetheless, the industrial revolution spurred fast scientific developments throughout the Enlightenment period, catalyzing a shift in science’s role towards addressing sensible challenges (Marburger, 2011). As a consequence, the system of scientific information, grounded in elementary ideas, theories, and mannequin legal guidelines, straight shapes technological innovation endeavors by guiding the group and amalgamation of particular technological information (Gibbons and Johnston, 1993; Zhao et al., 2023).
The affect of figuratively observing S&T interactions on expertise in quantitative evaluation might be traced again to the inception of quotation evaluation (Tijssen, 2001). This marked the starting of exploring S&T linkages by way of papers and patents (Narin and Olivastro, 1992; Ahmadpoor and Jones, 2017). The interconnectedness between papers citing patents, patents citing patents, and mutual citations between papers and patents constructs a complete community of S&T quotation relationships (Takano and Kajikawa, 2019; Choi and Yoon, 2022). However, the intricate nature of these networks, characterised by small-world buildings, power-law diploma distributions, hierarchical preparations, and cases of patents citing unrelated papers, poses challenges in using quotation evaluation for understanding S&T information group (Yi and Choi, 2011; Xu et al., 2022). To improve the discernment of S&T interplay traits, efforts have been made to include scientist and inventor community linkages (Breschi and Catalini, 2010; Li et al., 2020), together with IPC-ISI class mapping as extra specialised schemes (Han and Magee, 2018). Nevertheless, inherent biases in quotation practices, sparse creator networks, and the complexity of IPC-ISI class correspondence undermine the robustness of outcomes obtained by way of these methodologies in measuring precise S&T interactions (Xu et al., 2022). In response, approaches grounded in key phrase co-occurrence, topic-based evaluation, and information community coupling supply nuanced insights into S&T programs, enabling deeper understanding by way of built-in semantic and structural characterizations, thereby facilitating the efficient quantification of S&T interactions (Xu et al., 2019; Ba and Liang, 2021; Chen et al., 2023; Meng et al., 2023).
Burmaoglu et al. (2019) proposed that technological improvements possess qualitative novelty, synergy, pattern irregularity, excessive performance, and continuity. The affect of S&T information system interactions on technological innovation is multifaceted and multidimensional, encompassing combos, fusions, convergences, and divergences of information organizations over time and house. These function incubation circumstances for technological innovation (Shibata et al., 2010; Lee et al., 2018; Zhao et al., 2023). Synthesizing the interactive and synergistic options of S&T information programs for technological innovation represents an efficient technique for figuring out optimum S&T interplay websites and states.
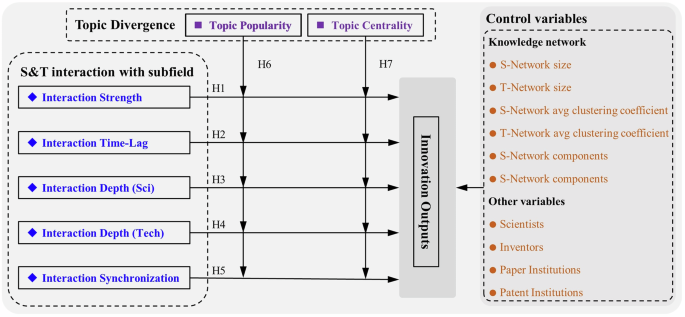
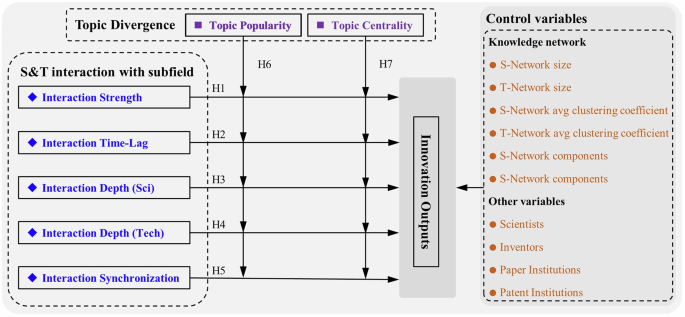
This research elucidates the role of S&T interplay in relation to technological innovation from two distinct views. First, we contemplate it by way of the lens of synergetics, which posits that regardless of diversified exterior properties, quite a few programs work together and cooperate inside a chaotic house (Haken, 1977). Self-organizing programs generate new temporal, spatial, or practical ordered buildings when subjected to exterior power, info, and materials movement inputs, facilitated by synergistic interactions with different programs. The infusion of scientific information disrupts the authentic homeostasis of the self-organizing technological construction, resulting in irregular patterns of growth (Brooks, 1994). Specifically, inside S&T interactions, the traits thereof hinge on the extent of information spillovers from each events, with extra harmonized domains exhibiting steady interplay traits however probably encountering stagnation in innovation momentum (Leydesdorff and Ivanova, 2020). Areas with scant theoretical information are inclined to expertise larger inflows of scientific information, whereas these in lead positions generate technological spillovers (Ba et al., 2024). Consequently, we analyze the traits of S&T interactions over time to discover their manifestation throughout the iterative transformation course of. Secondly, we discover this phenomenon by way of Piaget’s Theory, the place the dialectical interaction between heredity and setting intertwines by way of interactions, mutual influences, and transformations (Piaget, 1976). Consequently, innovation actions are influenced bidirectionally by each genetic elements (the innovation base) and environmental elements (the S&T interplay setting). By anchoring the impact of the S&T interplay setting, we additional look at whether or not domains with differing innovation bases affect the translational relationship between the S&T interplay setting and technological innovation. Thus, we assemble S&T information networks to ascertain hyperlinks between S&T elements and examine the affect of innovation foundations and the S&T interplay setting on technological innovation.
Impact of S&T interactions on technological innovation
S&T interplay power and innovation
Synergy, a elementary precept in synergetics elucidating the evolutionary legal guidelines governing programs (Haken, 1977), gives a beneficial lens for assessing the affect of interactions inside S&T programs on technological innovation efficiency. It is conceptualized as an intrinsic drive propelling the formation of structured programs, characterised by reciprocal inspiration and reinforcement amongst system assets as soon as a vital threshold is attained (Das and Jayaram, 2007). Typically, inter-organizational interactions are analyzed by way of marginal results, whereby the affect of a useful resource enter on efficiency is evaluated as the change ensuing from the funding of one unit of useful resource (Fan and Pan, 2023). Kelly et al. (2021) underscore the significance of prior technological endeavors, using textual content evaluation to hint the trajectory of technological developments throughout time. Zhao et al. (2023) assert the indispensability of pre-existing technological foundations for fostering innovation, highlighting a previous oversight in analysis that disregards the potential for innovation arising from scientific information. Consequently, to safe a sustainable aggressive edge, technological programs should harness information from numerous domains to reinforce their core competencies (Lee et al., 2018). However, prevailing analysis has predominantly examined the affect of S&T programs on technological innovation in isolation, pushed by a analysis paradigm targeted on addressing S&T gaps or using expertise categorization methodologies and roadmaps (Shibata et al., 2010; Burmaoglu et al., 2019; Sasaki and Sakata, 2020; Xu et al., 2021b). Our curiosity lies in elucidating how the power of interactions inside S&T information programs influences technological innovation.
Technology programs improve technological innovation efficiency by way of amalgamation and convergence. Those incorporating scientific information can combine a broader spectrum of assets (Lee et al., 2018). Specifically, a multi-domain, multi-topic S&T information system can flexibly converge present information throughout domains, fostering the emergence of extra applied sciences and alternatives (Li et al., 2021). Takano and Kajikawa (2019) confirmed the spillover results of scientific information, the place fast scientific developments precipitate technological improvements, usually resulting in their commercialization or widespread societal implementation in the close to future. Similarly, technological developments have propelled theoretical discoveries in science (Ba et al., 2024). Thus, S&T interactions can mitigate cognitive divergence stemming from information heterogeneity, thereby lowering prices related to information switch and communication, thus enhancing the effectivity of information integration and software in the innovation course of (Laursen and Salter, 2006). However, upon differentiating between novel expertise convergence (NTC, the place beforehand unconnected expertise fields converge) and strengthened expertise convergence (RTC, the allocation of multidisciplinary assets to established convergences), scientific convergence diminishes the optimistic affect of RTC on innovation efficiency (Zhao et al., 2023). Moreover, the objectives of scientific analysis and technological innovation diverge, and the escalating convergence of S&T information programs might devalue elementary analysis information in the eyes of innovation brokers, probably undermining technological innovation capabilities (Chen et al., 2023). These divergent views underscore the want for additional examination of the role of S&T interplay power on technological innovation. Thus, our research tentatively posits a optimistic relationship between S&T interplay power and technological innovation, as follows:
H1: S&T interplay power positively impacts technological innovation outputs.
Time-lag of S&T interplay and innovation
The slaving precept in synergetics, as elucidated by Haken (1977) and later expanded upon by Pecora and Carroll (1990), underscores the hierarchical relationship between quick and gradual variables inside system dynamics. It posits that fast variables conform to the affect exerted by slower variables throughout system interactions, with ordinal covariates exerting a dominant affect on system evolution. This precept manifests in system habits whereby swiftly dissipating groupings are compelled to synchronize with progressively rising groupings following proximity to a degree of instability or a vital threshold. In turbulent environments, the competing states of interacting programs rework converging tendencies, whereby their bistable traits evolve with a temporal delay, fostering an setting conducive to disruptive technological improvements (Broekstra, 2002). This temporal discrepancy in inter-system interactions can also be noticed in S&T programs, whereby science could precede expertise or vice versa (Ba and Liang, 2021; Yu et al., 2024). As the innovation cycle shortens, the nexus between expertise and fundamental science strengthens, enabling the detection of lag traits between S&T in the quick time period (Narin et al., 1997). The idea of the S&T hole delineates domains which are solely explored in science however stay underdeveloped in expertise, presenting vital potential for technological development (Shibata et al., 2010). This underscores the notion that the lag in expertise inside the S&T system carries alternatives for technological innovation (Shen et al., 2020; Ba et al., 2024). The time-lag state in S&T coupling emerges as a pivotal issue driving technological alternatives (Li et al., 2021). Consequently, domains the place expertise lags are more likely to exhibit larger revolutionary efficiency in collaborative endeavors in comparison with these the place S&T actions are carefully intertwined. Thus, we posit the following speculation:
H2: Time-lag state the place science leads expertise positively impacts technological innovation outputs.
S&T interplay depth and innovation
The self-organization principle inside synergetics gives a complete framework for understanding the structural evolution of each other-organized and self-organized programs (Haken, 1977; Corning, 2007). Self-organizing programs exhibit the capability to ascertain steady buildings or capabilities autonomously, devoid of exterior directives, by counting on inside subsystems ruled by particular guidelines. However, when infused with exterior power, info, and materials flows, these programs bear transformations, producing novel buildings which are temporally, spatially, or functionally ordered by way of synergistic interactions amongst quite a few subsystems (Kalantari et al., 2020).
Various domains, resembling the IPC classification construction of patents in technological programs (Sasaki and Sakata, 2020), quotation community buildings (Yi and Choi, 2011; Takano and Kajikawa, 2019; Choi and Yoon, 2022), and information attribute preparations (Song et al., 2017), manifest as steady self-organizing programs. Within hierarchical buildings of modular improvements, the potential for radical improvements at decrease technological tiers exists (Murmann and Frenken, 2006), and improvements at one degree could propagate to others (Sasaki and Sakata, 2020). The convergence of scientific information into technological programs is liable to affect the foundational information inside the technological hierarchy, reshaping its authentic construction by way of inherent synergies and thereby fostering revolutionary outcomes (Constant, 1987). Furthermore, Meng et al. (2023) noticed that S&T interactions predominantly happen inside related layers, indicating that scientific underpinning information tends to work together with technological underpinning information, and vice versa. Consequently, our research tentatively posits a optimistic affiliation between the depth of S&T interactions and technological innovation, proposing the following hypotheses:
H3: Depth of technology-to-science interplay positively impacts technological innovation outputs.
H4: Depth of science-to-technology interplay positively impacts technological innovation outputs.
Synchronization of S&T interplay and innovation
Synchronization denotes the upkeep of a constant relative relationship between two or extra evolving portions over time (Luo, 2009). In coupled oscillatory programs, each the sturdy coupling restrict and native coupling have the potential to disrupt synchronized chaotic oscillations (Heagy et al., 1994). S&T are inherently interdependent and intrinsically linked to societal growth and values (Amadi-Echendu, 2007). Consequently, intricate scientific ideas should evolve in tandem with technological practices, which, in flip, function sensible manifestations of scientific theories. Shibata et al. (2010) suggest that the relationship between S&T might be conceptualized as a course of of convergence, characterised by gradual synchronization. Furthermore, the accessibility and codification of scientific information allow technological organizations to derive advantages from convergence (Cardinal et al., 2001). Empirical proof from the U.S. pharmaceutical business signifies that an augmentation in the proportion of scientific information inside the S&T convergence course of correlates positively with innovation (Lee et al., 2018). Moreover, a excessive diploma of synchronization between S&T is deemed essential for innovation output (Leydesdorff and Ivanova, 2020). Thus, we posit the following speculation:
H5: Synchronization of S&T interactions positively impacts technological innovation outputs.
Moderating results of technological topic divergence
Piaget (1976) pressured the significance of each heredity and setting in growth, asserting that they don’t seem to be merely additive or confluent, however somewhat transformative and permeable. The present behavioral response to environmental stimuli emerges from the interaction between genetic inheritance and previous environmental experiences. Contingency principle additionally underscores the pivotal role of the setting in growth, positing that environmental uncertainty presents various indicators of alternative by way of modifications, which the system then exploits to generate worth (Lawrence and Lorsch, 1967).
S&T interactions engender a novel dynamic between S&T programs, which can manifest as technological innovation (Yan, 2014; Xu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023), scientific development (Ba et al., 2024), or a type of harmonious equilibrium (Shibata et al., 2010). However, scientific development depends predominantly on reasoning, argumentation, and logical help, whereas technological growth hinges on the integration and augmentation of present applied sciences (Xu et al., 2020), leading to substantial disparities in the preliminary genetic make-up of S&T programs. The breadth and depth of subjects in science, expertise, and innovation have been evolving, catalyzing cumulative improvements which will incite disruptive innovation revolutions (Small et al., 2014).
Divergence exists between scientists and inventors inside a area, resulting in wide-ranging opinions relating to the reputation of subjects in S&T, regardless of scientific literature surpassing patents in quantity. Addressing technical failures as a suggestions mechanism to spur fundamental science growth represents a extra scientifically widespread pursuit (Qi et al., 2018). This aligns with the notion that subjects having fun with scientific reputation usually tend to yield technological innovation efficiency. Zhang et al. (2016) equally recognized a optimistic correlation between comparatively widespread subjects and technological innovation by monitoring S&T topic interactions. Enhanced reputation of subjects could amplify the marginal impact of S&T interactions on technological innovation. Consequently, the following hypotheses had been formulated for our research:
H6: The affect of S&T interplay traits on technological innovation outputs is stronger in domains with greater technological topic reputation.
Key information ideas often function focal factors for analysis inside particular topic areas throughout specific cycles of scientific inquiry (Chen, 2005). In the realm of technological development, each the centrality index and the expertise cycle index discover utility, providing beneficial evaluation metrics for figuring out promising pathways in new product growth (Yoon and Park, 2004). Zamani et al. (2022) demonstrated that structural pore evaluation has been successfully employed to pinpoint core applied sciences (resembling “Internet of Things,” “Intelligent Transportation Systems,” and “Ultrasound”) inside sub-technological domains which have reached maturity, whereas additionally revealing nascent sub-topics inside rising expertise spheres by way of the utilization of low aggregation constraint values. Similarly, by way of topic modeling and social community evaluation of publications and patents, Kumari et al. (2021) illustrated the efficacy of topic key phrase centrality in elucidating the interrelations amongst subjects inside S&T, thereby figuring out evolving subjects and present focal factors, as exemplified in the research of “Humanoid Robot Technology.” Consequently, technological developments usually come up from rising fields and applied sciences encapsulating the most central subjects, with greater centrality fields amplifying the marginal impact of S&T interactions on innovation. Hence, our research posits the following speculation:
H7: The affect of S&T interplay traits on technological innovation outputs is stronger in domains with greater technological topic centrality.
The framework that underlies the empirical evaluation is proven in Fig. 1.