NCS
—
After many years of threats, Israel on Friday launched an audacious assault on Iran, focusing on its nuclear websites, scientists and army leaders.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu stated the operation had “struck at the head of Iran’s nuclear weaponization program.”
But worldwide assessments, together with by the US intelligence community, say that Iran’s nuclear program isn’t presently weaponized. Tehran has additionally repeatedly insisted it isn’t constructing a bomb.
Still, that doesn’t imply it couldn’t if it selected to.
Iran has spent many years growing its nuclear program and sees it as a supply of nationwide satisfaction and sovereignty. It maintains the program is solely for peaceable power functions and plans to construct further nuclear energy vegetation to meet home power wants and release extra oil for export.
Nuclear vegetation require a gas referred to as uranium – and in accordance to the UN nuclear watchdog, no different nation has the type of uranium that Iran presently does with out additionally having a nuclear weapons program.
That has fueled suspicions that Iran isn’t being totally clear about its intentions. Tehran has used its stockpile of weapons-grade uranium as a bargaining chip in talks with the United States, repeatedly saying it will do away with it if US-led sanctions are lifted.
So, what precisely is uranium’s function in a nuclear weapon, and the way far is Iran from weaponizing its program? Here’s what you want to know.
The US launched a nuclear program with Iran in 1957. Back then, the Western-friendly monarch – the Shah – dominated Iran and the 2 international locations have been nonetheless pals.
With backing from the US, Iran began growing its nuclear energy program within the Seventies. But the US pulled its assist when the Shah was overthrown throughout the Islamic Revolution in 1979.
Since the revolution, which reworked Iran into an Islamic Republic, Western nations have apprehensive the nation may use its nuclear program to produce atomic weapons utilizing extremely enriched uranium.
Iran has maintained that it doesn’t search to construct nuclear weapons. It is a celebration to the UN’s Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), beneath which it has pledged not to develop a bomb.
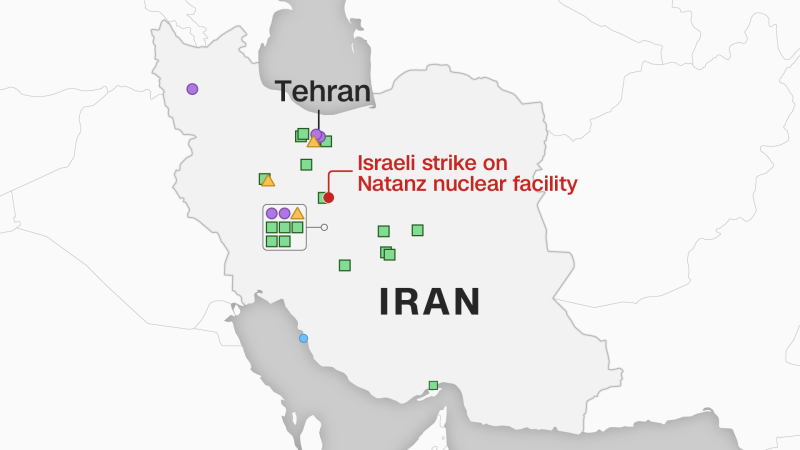
Here’s the place its nuclear services are situated.
At the center of the controversy over Iran’s nuclear program is its enrichment of uranium – a course of used to produce gas for energy vegetation that, at increased ranges, can be used to make a nuclear bomb.
In the early 2000s, worldwide inspectors introduced that they’d discovered traces of extremely enriched uranium at an Iranian plant in Natanz. Iran briefly halted enrichment, however resumed it in 2006, insisting it was allowed beneath its settlement with the UN’s nuclear watchdog, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
It prompted years of worldwide sanctions towards Iran.
After years of negotiations, Iran and 6 world powers in 2015 agreed to a nuclear deal that restricted Iran’s nuclear risk in return for lighter sanctions.
The deal required Iran to hold its uranium enrichment ranges at not more than 3.67%, down from close to 20%, dramatically cut back its uranium stockpile, and section out its centrifuges, amongst different measures.
Uranium isn’t bomb-grade till it’s enriched to 90% purity. And nuclear energy vegetation that generate electrical energy use uranium that’s enriched to between 3.5% and 5%.
It’s unclear how shut Iran is perhaps to really constructing a nuclear bomb, if in any respect, however it has made important progress in producing its key ingredient: extremely enriched uranium. In current years, it has sharply decreased the time wanted to attain weapons-grade ranges – now requiring simply about per week to produce sufficient for one bomb.
In 2018, Trump pulled out of the Iran nuclear deal and initiated new sanctions on the regime to cripple its economic system.
Tehran in flip stated it will stop complying with elements of the settlement, and began rising uranium enrichment and uranium stockpiles, and utilizing superior centrifuges.
It eliminated the entire IAEA gear beforehand put in for surveillance and monitoring actions.
The Biden administration then kicked off greater than a 12 months of oblique negotiations with Iran aimed toward reviving the deal, however these broke down in 2022.
In 2023, the IAEA stated uranium particles enriched to 83.7% purity – shut to bomb-grade ranges – have been discovered at an Iranian nuclear facility. Its stockpile of uranium enriched up to 60% had additionally grown to 128.3 kilograms, the highest level then documented.
And final 12 months, the US shortened Iran’s so-called “breakout time” – the period of time wanted to produce sufficient fissile materials for a nuclear weapon – “to one or two weeks.”
An IAEA report despatched to member states late final month stated Iran’s inventory of 60% purity enriched uranium had now grown to 408 kilograms. That is sufficient, if enriched additional, for 9 nuclear weapons, in accordance to an IAEA yardstick.
The IAEA has lengthy accused Iran of violating its non-proliferation obligations, however on Thursday – for the primary time in virtually 20 years – its board handed a decision formally declaring Iran in breach of these obligations. Iran promised to reply by escalating its nuclear actions.
Enrichment is a course of that will increase the quantity of uranium-235, a particular kind of uranium used to energy nuclear reactors or, in a lot increased quantities, to make nuclear weapons.
Natural uranium is usually uranium‑238 – about 99.3%, which isn’t good for energy or bombs. Only about 0.7% is uranium‑235, the half wanted to launch power.
For nuclear power use, that tiny quantity of helpful uranium-235 wants to be concentrated. To do that, uranium is first become a fuel, then spun at excessive speeds in machines referred to as centrifuges. These machines assist separate uranium-235 from the extra frequent uranium-238. That is what enrichment is.
Uranium utilized in nuclear energy vegetation is usually enriched to about 3.67%. To make a nuclear bomb, it wants to be enriched to round 90%. Iran has enriched uranium to 60% – not sufficient for a bomb, however a serious step nearer to weapons-grade materials.
Centrifuges are important for enriching uranium. The extra superior the centrifuge, the quicker and extra effectively it might probably separate uranium-235 from uranium-238 – shortening the time wanted to produce nuclear gas or, doubtlessly, weapons-grade materials. Iran has spent many years bettering its centrifuge expertise, beginning with its first-generation IR-1 mannequin within the late Nineteen Eighties. Today, it operates 1000’s of machines, together with superior fashions just like the IR-6 and IR-9.
According to the Arms Control Association, Iran’s present centrifuge capability may enable it to produce sufficient weapons-grade uranium for a bomb in lower than two weeks.
Israel says it’s focusing on Iran’s nuclear infrastructure in its assault.
Natanz, the ability on the coronary heart of Iran’s nuclear ambitions, was engulfed in flames on Friday, in accordance to social media pictures geolocated by NCS and Iranian state tv protection.
The nuclear advanced there, about 250 kilometers (150 miles) south of the capital Tehran, is taken into account Iran’s largest uranium enrichment facility. Analysts say the location is used to develop and assemble centrifuges for uranium enrichment, a key expertise that turns uranium into nuclear gas.
The IAEA stated three nuclear websites, Fordow, Isfahan and Bushehr, had not been impacted.
Six of Iran’s nuclear scientists have been additionally killed in Israel’s strikes, Iranian state-affiliated Tasnim information company stated.
Iran has spent years strengthening its nuclear buildings towards the specter of army strikes, which is able to make it tough to comprehensively destroy them, army specialists have instructed NCS.
Some services are buried deep underground to put them out of attain of Israel’s weapons.