The Department of Energy (DOE) has renewed funding for the Quantum Systems Accelerator (QSA), a DOE National Quantum Information Science Research Center led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) in partnership with Sandia National Laboratories. QSA builds and demonstrates quantum applied sciences and computing prototypes to rework quantum data science into breakthroughs for society. These advances will allow scientists to make use of quantum computer systems to design new supplies, uncover new chemical substances and reactions, and speed up breakthroughs in vitality, physics, biology, and chemistry.
The whole deliberate funding for QSA is $125 million over 5 years, with $25 million in yr one and out-year funding contingent on congressional appropriations.
QSA is one in all 5 National Quantum Information Science (QIS) Research Centers established by DOE in 2020 to broaden the frontier of what is attainable in quantum computing, communication, sensing, and supplies in methods that can advance primary science for vitality, safety, communication, and logistics. Together, the facilities have strengthened the nationwide quantum data science ecosystem, achieving scientific and technological breakthroughs in addition to coaching the next-generation quantum workforce. DOE has renewed funding for all 5 facilities.
QSA brings collectively 15 associate establishments in North America to drive quantum expertise ahead. The middle combines world-leading experience and capabilities throughout nationwide labs, academia, and {industry}. QSA may even associate with {industry}, similar to Nobel Prize winner John Martinis’ Qolab, to advance quantum expertise for DOE and business purposes. These public-private partnerships will make sure that QSA’s science and expertise advances are industry-relevant at each stage.
Among QSA’s many achievements in its first 5 years, the middle made world-leading developments on three promising qubit applied sciences: trapped ions, impartial atoms, and superconducting circuits. These achievements are laying the muse for constructing sensible quantum programs that may deal with real-world scientific and vitality challenges and have strengthened QSA’s function in holding the U.S. on the forefront of transformative quantum applied sciences.
“QSA plays a vital role in advancing QIS across the U.S. by bridging the gap between national labs, academia, and industry. By fostering collaboration, QSA ensures that breakthroughs can move from experimental stages to practical applications, benefiting the nation,” stated QSA Director and Berkeley Lab scientist Bert de Jong.
“Quantum information science and technology promises to deliver transformative solutions for the nation’s most critical scientific and energy challenges. QSA will help realize this future by co-designing the algorithms, devices, and engineering innovations that will make quantum solutions possible,” stated Carol Burns, Deputy Lab Director for Research at Berkeley Lab.
“We stand at a pivotal moment in our pursuit of quantum utility. By developing next-generation quantum computing prototypes and scalable technologies, we are not only pushing the boundaries of quantum science; we are transforming these advancements into practical solutions for critical applications that will shape our future. Together, we are empowering American innovation,” stated Sandia National Laboratories’ Christopher DeRose and QSA deputy director.

Next up: Improve efficiency a thousand fold, and extra
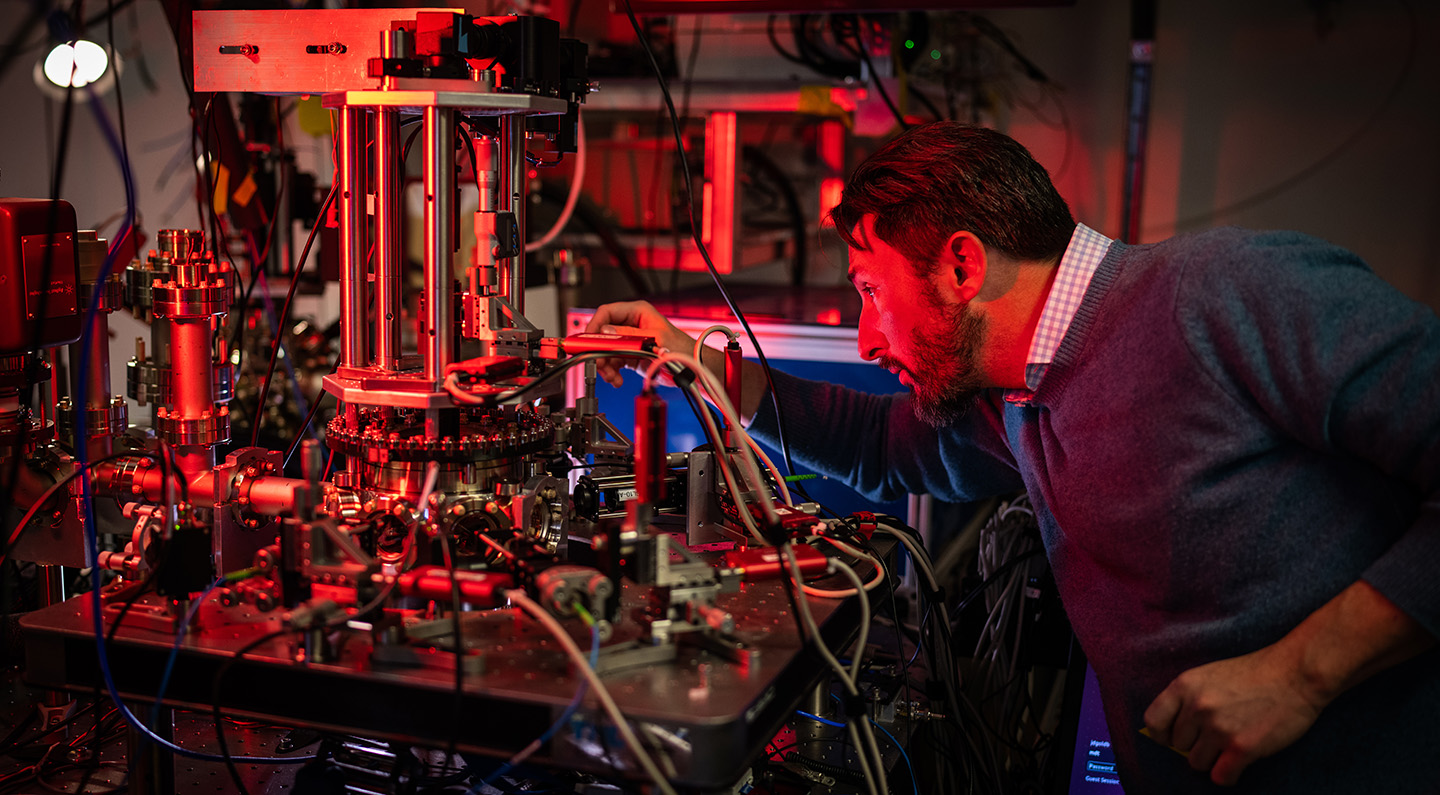
Over the subsequent 5 years, QSA’s analysis will deal with two large targets: constructing working prototype quantum gadgets that may clear up scientific challenges past the attain of standard computer systems, and – in shut partnership with {industry} – creating applied sciences that make quantum programs dependable and scalable for on a regular basis use. With an bold goal of attaining 1,000-fold efficiency beneficial properties in quantum computational energy by 2030, QSA is co-designing scalable programs and benchmarking strategies to push the boundaries of what quantum computer systems can obtain. To get there, they’re scaling up the variety of usable qubits and considerably bettering their reliability.
For impartial atom programs, QSA scientists goal to construct machines holding extra atoms that, when mixed with error correction, can run 1,000 instances extra advanced calculations with excessive constancy than present programs. For trapped ions, they’re creating new methods to encode data that may deal with 100 instances extra information. And for superconducting circuits, they’re bettering management programs and decreasing the variety of qubits wanted for error correction to realize a 1,000-fold acquire in computational energy. Across all platforms, QSA can be creating new benchmarking approaches to correctly validate the efficiency of quantum computer systems, advance error correction, and construct smarter algorithms to completely make the most of these {hardware} breakthroughs.
Building on 5 years of QSA achievements
Since launching in 2020, QSA has enabled main advances in quantum data science, together with record-setting sensors, smarter algorithms, and extra. QSA achieved a serious milestone by being the primary to develop and function atom-based quantum simulators with over 200 qubits, whereas additionally advancing superconducting processors and trapped-ion applied sciences. QSA researchers additionally built quantum devices so exact they’ll detect tiny adjustments in Earth’s gravity, and created quantum error-correcting methods that deliver scientists nearer to fault-tolerant quantum computer systems.
QSA’s initiatives have led to over a dozen patents, numerous scientific publications, and the creation of startups which are bringing quantum expertise to the market. Multiple quantum companies have benefited from QSA’s in depth analysis community and ongoing collaborations, using the experience, suggestions, and methods shared by QSA companions to reinforce their processes. Additionally, 5 QSA principal investigators have co-founded quantum firms, making use of analysis outcomes to promising {industry} use instances.
QSA has additionally skilled a new generation of scientists and engineers, lots of whom at the moment are main quantum analysis at prime firms and universities, alongside high school college students and academics. In addition to the 150 graduate college students and 100 postdoctoral college students delivering leading edge analysis in QSA yearly, QSA’s QCaMP program has launched quantum to over 160 highschool academics and three,200 college students throughout the nation. Building on this success, QSA will assist create a quantum-ready workforce with new pathways and partnerships that have interaction undergraduates in group schools through hands-on coaching applications.
To study extra about QSA’s many achievements, this article highlights 5 methods QSA has superior quantum computing. And this Q&A with de Jong showcases QSA’s progress, thrilling plans for the longer term, and the sorts of breakthroughs to anticipate as quantum programs develop and mature.
Leveraging QSA’s experience and capabilities
QSA develops next-generation quantum capabilities by integrating multidisciplinary groups throughout its associate establishments and leveraging specialised quantum-ready amenities at Berkeley Lab, Sandia National Laboratories, and different main establishments.
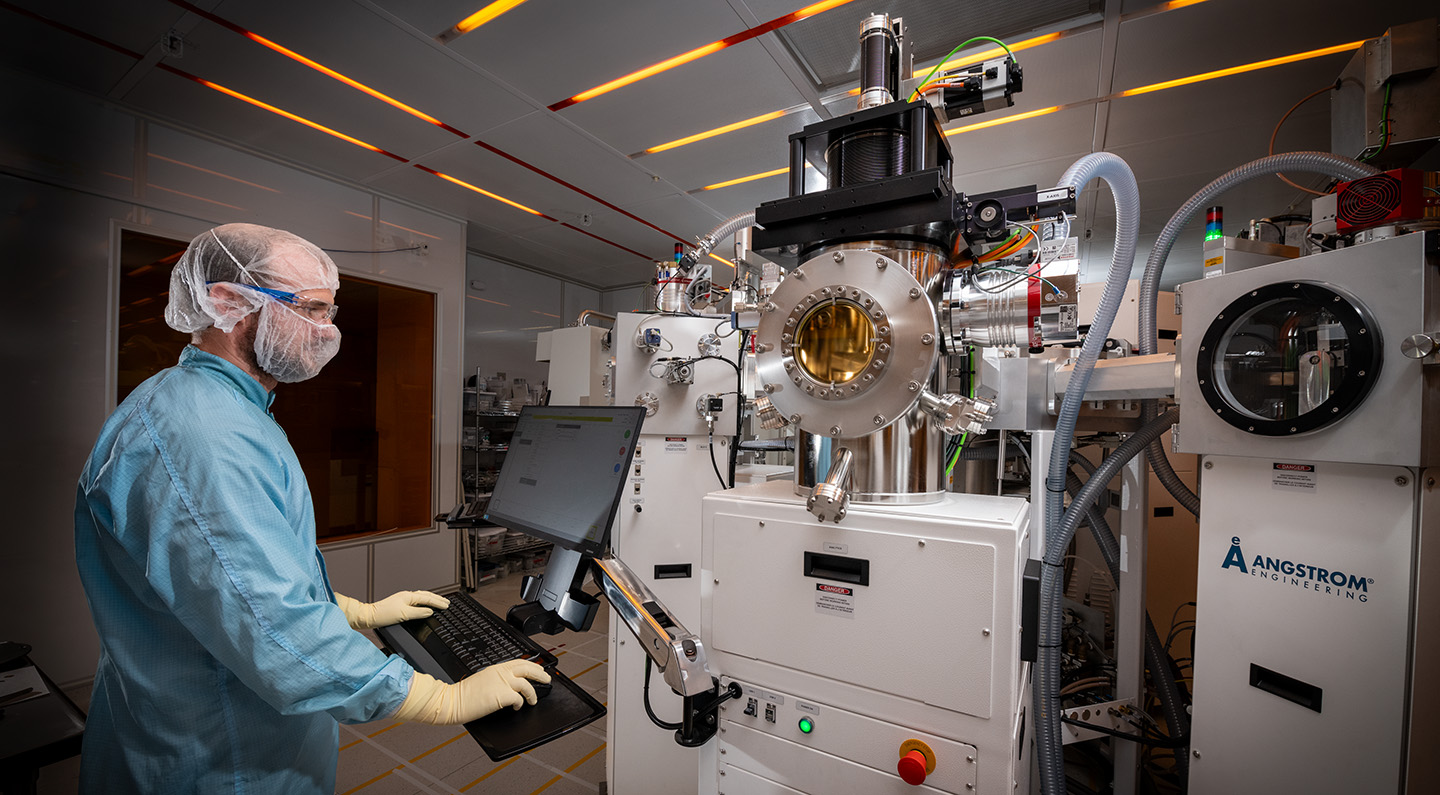
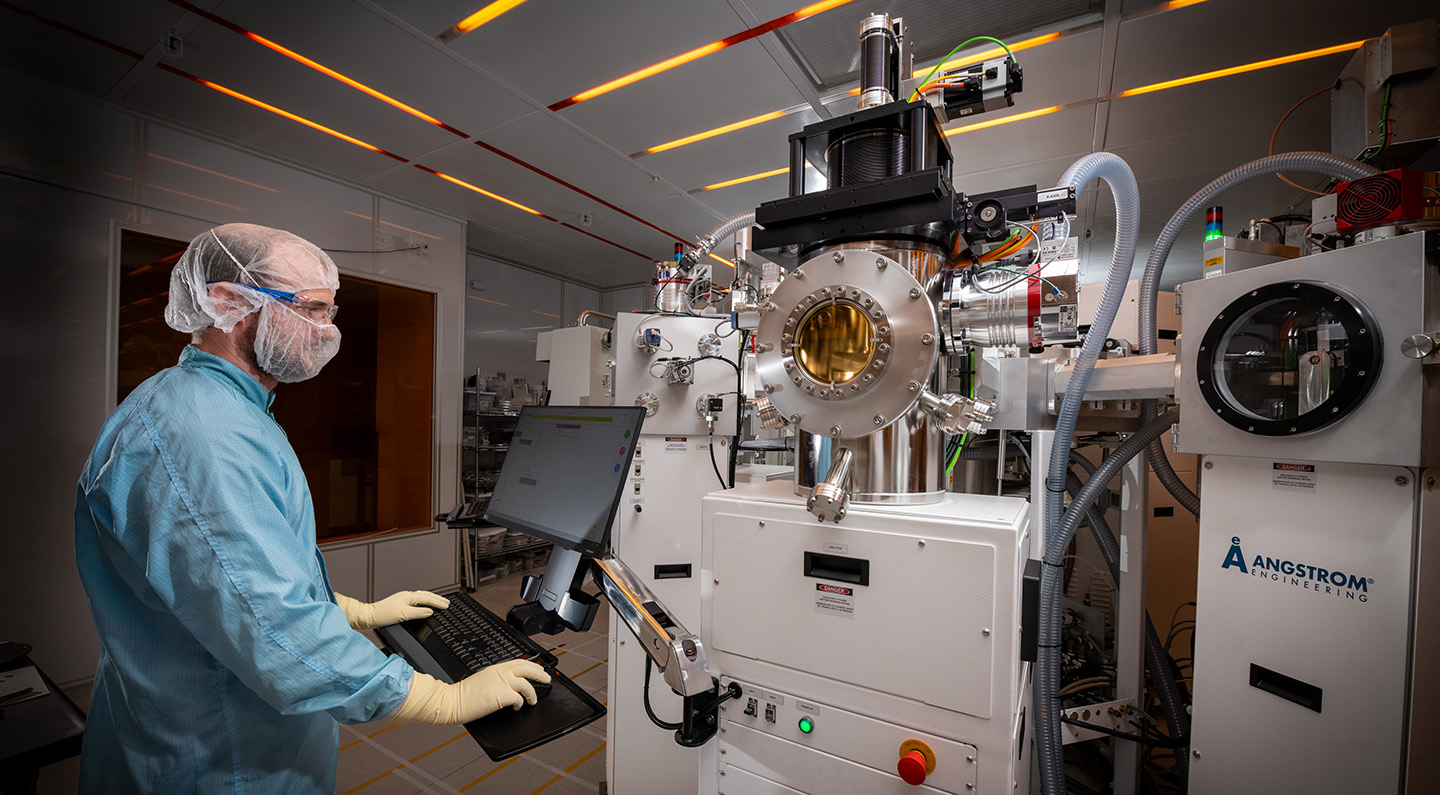
Berkeley Lab, for instance, companions with {industry} and academia and works throughout the quantum analysis ecosystem – from theory to application – to manufacture and take a look at quantum-based gadgets, develop software program and algorithms, and construct prototype computer systems and networks. Berkeley Lab’s nationwide person amenities present state-of-the-art assets for scientists in QSA and past to advance the frontiers of quantum science. This consists of the Advanced Light Source, the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), and the Molecular Foundry, which has a QIS cluster instrument that allows researchers to experiment with dozens of supplies and strategies for making qubit parts in a single automated system. The Molecular Foundry may even quickly add a dilution fridge that can allow high-throughput evaluation of qubits. Berkeley Lab additionally leads the Advanced Quantum Testbed (AQT), a collaborative analysis laboratory and open-access testbed to advance quantum computing based mostly on superconducting circuits. In this video, de Jong, shares how quantum analysis at Berkeley Lab is forging the way forward for quantum breakthroughs by collaborating with researchers throughout establishments.