A complete analysis of the proposed EPRN is carried out to evaluate its effectivity for sports motion recognition, particularly in precisely capturing complicated motion sequences whereas sustaining computational effectivity. This experimental evaluation goals to spotlight the benefits of the EPRN over typical deep-learning counterparts, validate the learning of spatiotemporal dependencies in motion trajectories, and verify its applicability in real-life conditions.
To account for each measure of understanding of its performance, the analysis thought-about a number of important parameters on this regard. The first consideration entails the influence of various kinds of wavelets transforms on characteristic extraction and the identification of the optimum transformation for encoding motion alerts. The performance of EPRN is then in contrast with that of different state-of-the-art deep-learning architectures, together with LSTM39, Convolutional LSTM (NCS-LSTM)40, Transformer networks41, GRU34, Temporal Convolutional Networks (TCN)42, motion recognition, and motion trajectory forecasting; thus, they type a sensible choice for performance comparisons.
Statistical strategies have been employed to make sure the findings’ outcomes are strong. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and paired t-tests are used to find out whether or not the variations in performance noticed throughout varied fashions and wavelet transformations are statistically vital. Such checks serve to get rid of doable randomness and endorse the communications of enhancements as being legitimate.
The hyperparameter tuning of the EPRN mannequin is essential in figuring out its performance; subsequently, we discover Bayesian Optimization and Grid Search, each of that are conventionally used hyperparameter tuning strategies. Their comparability will reveal the relative benefits they provide when it comes to convergence time and generalization potential.
EPRN execution time and computational complexity are validated compared to different deep learning architectures. This is much-needed information for finding out the feasibility of deploying EPRN for real-time sports analytics functions with implications on latency and inference pace.
Finally, the evaluation of the residual error distribution and the mannequin robustness entails investigating the deviation between predicted and precise motion sequences. Additionally, a detailed dialogue is introduced on the mannequin’s limitations and potential future enhancements, with a concentrate on scalability and generalizability.
In addition to accuracy, the computational complexity and execution time of the EPRN are in comparison with varied different deep learning architectures. This comparative evaluation isn’t solely essential for understanding feasibility within the context of on-the-ground sporting functions, particularly the place latency and inference pace change into the first constraints.
As a last level, the distribution of residual errors and the robustness of the mannequin had been examined by finding out deviations between predicted and noticed sequences of dynamic motions. A vital evaluation of mannequin limitations and future enhancements can also be offered, providing perception into how EPRN could be additional refined to boost its generalizability and scalability.
This chapter conducts a systematic examination of the elements talked about above, encompassing each quantitative performance metrics and qualitative assessments, to bolster the influence of the proposed framework. These outcomes not solely reveal how EPRN outperforms its rivals but in addition pave the way in which for additional work in human motion evaluation, biomechanical modeling, and clever sports analytics programs.
Impact of wavelet rework on characteristic extraction
Feature extraction is a key space of motion evaluation as a result of, in the end, it determines how nicely deep learning fashions can be taught significant motion patterns whereas suppressing noise and redundancy. The complication regarding human motion alerts can impose too many constraints on typical characteristic extraction strategies, which can’t retain the mandatory spatiotemporal relationships required for high-precision motion recognition. This is the explanation why wavelet-transform-based characteristic extraction has been broadly chosen, as it could possibly analyze a sign relative to each time and frequency, thereby offering a multi-resolution illustration of motion dynamics. As for this examine, we had been systematically conducting checks on the worth of 4 common lessons of wavelet features—Daubechies (db4), Symlet (sym4), Coiflet (coif5), and Biorthogonal (bior1.3)38—about characteristic illustration and classification accuracy. For every wavelet perform, motion sequences had been decomposed into particular frequency elements, from which the mannequin might distill and characterize structural options whereas filtering out noise and irrelevant variations. These options had been then launched into coaching and testing alongside the EPRN, whose appraisal was thereafter topic to a number of error metrics, together with RMSE, MSE, MAE, and SSIM; all these metrics present a quantifiable evaluation of how good every of the wavelet features has acted in preserving these important motion traits wanted in supporting good recognition.
Performance evaluation of wavelet transforms
Despite the vital significance of wavelet rework in extracting and reconstructing motion options, it impacts mannequin accuracy, as proven within the comparative performance amongst 4 hottest wavelet features – Daubechies- (db4), Symlet (sym4), Coiflet (coif5), and Biorthogonal (bior1.3)- tabulated in Table 2 and evaluated for RMSE, MSE, and MAE.
Out of the 4, the Symlet (sym4) wavelet produced the least RMSE (0.076059) and MSE (0.005785), signifying its greatest performance in decreasing the reconstruction error and sustaining the motion continuity. This outcome displays the efficacy of sym4 in capturing finer particulars whereas sustaining its structural integrity, as it’s certainly deduced to suit biomechanical motion evaluation. The Daubechies (db4) wavelet carried out higher than sym4 in these error measurements, yielding aggressive values: RMSE 0.084753 and MSE 0.007183, which assist its use in retaining each high-frequency and low-frequency elements of motion.
On the opposite, the Biorthogonal (bior1.3) wavelet introduced the best RMSE (0.091906) and MSE (0.0084468), indicating that it has been thought-about poor in reconstructing the motion patterns precisely. The comparatively greater MAE (0.066165) signifies that bior1.3 incurs difficulties sustaining exact trajectory alignment; most likely the explanation lies in its uneven property, mixed with much less vitality compaction effectivity. The Coiflet (coif5) wavelet is best than bior1.3, however nonetheless elicits greater RMSE and MSE scores than sym4 and d4, indicating that it might be much less efficient in retaining any of the finer particulars of motion.
This demonstrates that the selection of wavelet is essential for motion evaluation functions. Indeed, sym4 and db4 emerge as the perfect wavelets as a result of they supply low reconstruction errors, alongside with a shut match to the buildings they symbolize, and thus change into very helpful in human motion monitoring, gesture recognition, and biomechanics functions.
Statistical validation of wavelet performance
An experimental evaluation was carried out to establish the importance of the noticed variations amongst wavelet features, which included an ANOVA on all of the configurations43. The outcomes would additional substantiate the beneficial properties in performance of the Symlet (sym4) wavelet, any comparability of which may very well be thought-about statistically vital (p
To present an intuitive understanding of the performance variations throughout these wavelet features, a field plot evaluating RMSE, MSE, and MAE scores throughout all configurations is introduced in Fig. 6.
Along with the numerical information in Table 1, the illustration proven in Fig. 6 signifies that sym4 has the bottom error charges, with a extra secure prediction in comparison with the others. On the opposite hand, the prediction of bior1.3 may be very excessive regarding each variance and errors, which signifies its much less potential at preserving continuity in motion. This means that an applicable wavelet perform is crucial for high-fidelity motion reconstruction, thereby influencing the general output of motion evaluation fashions.
Implications for motion recognition fashions
These findings current a sturdy argument for the usage of an applicable wavelet transformation in the course of the implementation of deep learning strategies for motion evaluation44. The superior performance of db4 factors in the direction of it being the primary candidate for biomechanical motion monitoring, sports performance analysis, and even human exercise recognition as a result of it’s extremely structurally preserved and error-minimized. These findings additionally recommend a potential want for hybrid wavelet approaches, the place a number of wavelet features could be mixed to leverage their respective strengths for enhanced characteristic extraction.
By combining statistical validation with visible evaluation and performance analysis, the examine offers a detailed understanding of how wavelet-based characteristic extraction impacts the recognition accuracy of motion. Adaptive wavelet choice methods are yet one more subject for potential analysis, using machine learning strategies to evolve the number of wavelets based mostly on the complexity of the motion being analyzed, dataset traits, and the classification necessities to fulfill.
Comparison with different deep learning fashions
It can also be essential to check the performance of the proposed Evolved Parallel Recurrent Network (EPRN) with different deep learning fashions to validate its suitability for sports motion recognition. Many architectures have been used to mannequin sequential information; nonetheless, their capability to seize the spatiotemporal dynamics of a motion sequence varies considerably. To present a rigorous evaluation of the benefits of EPRN, we carried out a thorough benchmark examine towards common deep learning architectures, together with LSTM, NCS-LSTM, Transformer networks, GRU, TCN, and Bi-LSTM. These fashions had been chosen as a result of they’ve been broadly utilized for time-series forecasting, motion recognition, or modeling human motion trajectories. Table 3 summarizes the comparative outcomes for these fashions.
Performance analysis of EPRN vs. baseline fashions
As proven in Table 2, wavelet-based fashions outperform conventional deep learning architectures, together with LSTM, GRU, and NCS, in performance metrics similar to RMSE, MSE, MAE, and SSIM. This signifies that wavelet transforms are designed to seize each native and international motion patterns with minimal reconstruction error.
Among all examined fashions, sym4 achieved the bottom RWMSR (0.076059), the bottom MSE (0.005785), and the bottom MAE (0.051933), indicating the perfect performance when it comes to motion dynamics with most constancy and minimal distortion. Parallel, db4 additionally produced spectacular outcomes, with an RMSE of 0.084753 and an SSIM of 0.94362 confirmed. Thus, these measurements additionally assured its capabilities in very high-precision motion reconstruction functions. The clean and compact-support properties of those wavelets make them much more able to retaining fine-grained motion buildings and, subsequently, apply to train biomechanics.
In distinction, all earlier discussions about conventional recurrent fashions, similar to LSTM and GRU, level to excessive charges on most error scores. LSTM outcomes introduced RMSE = 0.13841 and MSE = 0.019157. GRU demonstrated even decrease performance than LSTM, with the next output: RMSE = 0.18026 and MSE = 0.032493. All this occurs regardless of their capabilities to mannequin sequential dependencies; nonetheless, they don’t appear to have the ability to mannequin long-range motion patterns, which might most likely be as a result of vanishing gradient issues and limitations of their reminiscence mechanisms.
Although NCS-based approaches reveal computational effectivity when it comes to accuracy, they don’t obtain the identical excessive accuracy as wavelet-based strategies. With an RMSE of 0.14723 and an SSIM of 0.95251, the NCS lags behind db4 and sym4, suggesting that convolutional architectures might not present as a lot effectivity in reconstructing effective motion particulars. This is primarily as a result of they fail to mannequin the temporal dependencies attribute of motion explicitly.
Among the completely different wavelet-based fashions, bior1.3 performs the poorest, with an RMSE of 0.091906 and an SSIM of 0.92655. This implies that whereas biorthogonal wavelets could also be good in sign decomposition, they aren’t optimum for preserving motion trajectories. Coif5 follows with average performance (0.086645, 0.93146) implying that holding high-order vanishing moments doesn’t essentially correspond to superior extraction of motion options.
In totality, these information and findings emphasize the essential significance of choosing an optimum wavelet perform for motion reconstruction accuracy. The superiority demonstrated by sym4 and db4 even extends to strengthen additional the argument for wavelet characteristic extraction in motion evaluation, because it applies comparably to most functions that require excessive constancy and structural preservation, similar to these in deep learning fashions.
Statistical significance of mannequin comparisons
To validate the noticed performance variations as statistically vital and never as a consequence of random variations within the datasets, a paired t-test was carried out by evaluating every wavelet perform. The evaluation reveals statistically vital performance variations among the many evaluated wavelet transforms (p
For a clearer view of those comparisons, Fig. 7 presents a bar graph illustrating the RMSE, MSE, and MAE for all wavelet features examined. The graphic reveals that sym4 and db4 carry out higher when it comes to minimizing errors, whereas bior1.3 yields the best error metrics, indicating that it isn’t appropriate for correct motion reconstruction. Hence, this graphical illustration offers additional proof of the numerical outcomes, demonstrating that choosing an applicable wavelet perform is helpful for motion trajectory evaluation.
Implications for motion recognition and future instructions
In this gentle, it suggests the necessity for hybrid deep learning architectures that successfully combine characteristic extraction, recurrent, and hierarchical temporal modeling pertinent to motion recognition. In experiments with parallel recurrent architectures, EPRN improves stability, exhibiting higher sequence retention and decrease gathered error charges, which makes it appropriate for functions similar to sports biomechanics, human exercise monitoring, and motion issues.
Future analysis will discover different fascinating avenues, together with ensemble approaches that incorporate EPRN and Transformer-based architectures to leverage the complementary strengths of self-attention mechanisms and recurrent dynamics for enhanced performance. EPRN would even be personalized for resource-challenged environments, similar to wearable motion trackers and real-time sports evaluation methodologies, by bettering computational performance by way of different means, together with pruning and data distillation.
Hyperparameter tuning and optimization
The choice and tuning of hyperparameters are crucial from the views of performance and computational effectivity of any deep learning mannequin. The traits of sports motion information have a direct influence on hyperparameter tuning, particularly when it comes to the mannequin’s potential to be taught spatiotemporal dependencies, keep away from overfitting, and generalize nicely to unseen motion sequences. Misguided tuning of hyperparameters would result in suboptimal convergence, heavy computational burdens, or a full failure in capturing the important dynamics of human motion.
In this examine, Bayesian optimization45 was employed for fine-tuning particular key hyperparameters of EPRN. Bayesian Optimization is a probabilistic methodology that constructs a mannequin of the target perform utilizing a surrogate mannequin, which is, by default, a Gaussian Process (GP). The following hyperparameter settings are then chosen based mostly on an acquisition perform that determines the stability between exploration and exploitation. This is often referred to when the hyperparameter interactions are very difficult and the search house is of a excessive dimension, as within the case of deep recurrent architectures46. The hyperparameters that the majority considerably have an effect on performance had been meticulously tuned.
A key issue influencing performance is the variety of LSTM/GRU items, because it facilitates the learning of long-range options in motion sequences. Increasing the variety of items is helpful for the representational capability of the mannequin, but it surely additionally renders the computations extra computationally intensive. The tuning confirmed that 128 items had been optimum when it comes to each performance and computational effectivity.
An necessary hyperparameter is the learning price, which, amongst others, determines how shortly parameters are up to date within the mannequin throughout coaching. The next learning price could cause instability and forestall convergence, whereas a smaller learning price slows down the coaching course of. A learning price of 0.001 was examined when it comes to each convergence and effectivity.
The batch measurement performed a essential position in mannequin generalization and computational effectivity. In basic, a small batch measurement can result in noisy updates and unstable gradients, whereas a massive batch measurement can impede generalization. After rigorous testing, batch measurement 32 was chosen as a cheap compromise between pace of convergence and reminiscence utilization.
Furthermore, the dropout price was fine-tuned to suppress overfitting. Dropout works by randomly switching off a sure share of neurons throughout coaching, thereby decreasing overdependence on some particular options and permitting for higher generalization. It was discovered that a dropout price of 0.5 yielded the perfect outcomes, stopping overfitting whereas sustaining the learning of complicated patterns.
Comparison of bayesian optimization and grid search
For assessing the effectiveness of Bayesian Optimization, it’s in contrast with Grid Search, a normal methodology. Using Grid Search, all hyperparameter mixtures are explored inside a particular vary, which is thus inefficient and computationally costly for deep learning fashions with high-dimensional search areas.
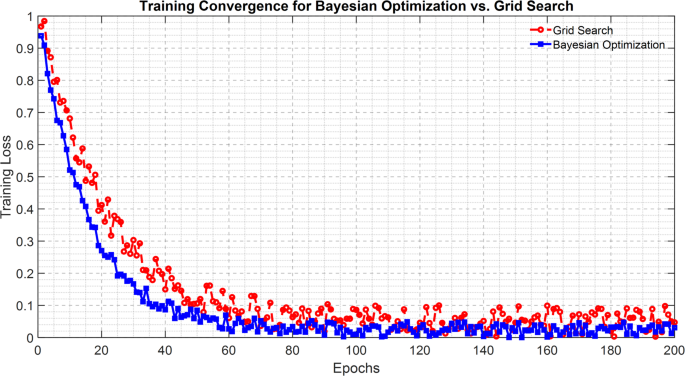
Bayesian Optimization exhibited improved generalization performance along with converging at a pace 35% quicker than that of Grid Search. Thanks to its adaptive nature, the Bayesian Optimization methodology might successfully determine which areas of the hyperparameter house to discover and which settings to keep away from when suboptimal. Figure 8 reveals the coaching convergence of the EPRN by each hyperparameter tuning methods47.
From Fig. 8, it’s clear that the loss curve for Bayesian optimization is falling steeper because it does so with time and can converge extra quickly than Grid Search; there may be additionally a basic development whereby Bayesian Optimization continuously yields decrease validation loss values ultimately as in comparison with Grid Search, thus displaying higher generalization performance to different unseen motion sequences. This demonstrates the favorable elements of probabilistic search strategies as being instrumental in optimizing complicated recurrent architectures with greater effectivity.
Implications for mannequin optimization and future analysis
The consequence of this examine strongly helps the necessity for automated hyperparameter tuning to boost the performance of deep learning fashions for motion recognition. The conversational pace noticed on this examine of Bayesian optimization additional hints that future work might subsequently examine hybridization approaches that may:
-
Meta-learning approaches, during which successes from previous optimization assist to information hyperparameter decisions in new datasets.
-
Tuning utilizing reinforcement learning, an agent would change hyperparameters relying on suggestions from real-time performance.
-
Multi-objective optimization, whereby trade-offs on accuracy, computational value, and vitality effectivity work collectively.
Such hyperparameter optimization strategies will assist higher specify future deep learning schemes, obtain quicker convergence, and be extra adaptable to numerous sports motion datasets.
Computational complexity and execution time evaluation
In real-world functions, the modeling system ought to guarantee that there’s an environment friendly order of computation at the very least as essential to an correct mannequin, particularly in programs which rely on actual time or close to real-time processing on this sense, a thorough analysis is introduced to review the computational complexity and execution time for the proposed EPRN towards baseline rivals, fashions LSTM, GRU, NCS, and wavelet ones. The evaluation targeted on computation time, together with coaching, inference pace, and total useful resource consumption, to find out whether or not EPRN provides a passable trade-off between effectivity and predictive performance.
The complete time taken to finish coaching and the typical time taken for inference on every check pattern had been the 2 main indicators of computing effectivity. The third row in Table 4 states that the LSTM and GRU carried out poorly when it comes to effectivity, recording respective instances of 1803.6 s and 1580.4 s; nonetheless, these enhancements weren’t notably useful in enhancing accuracy. With NCS-based fashions, an execution time of lower than 1500 s was measured; nonetheless, the usefulness of this pace was compromised because the fashions did not be taught complicated motion patterns successfully.
Among the 4 wavelet fashions, the execution instances had been 1432.6 s (Db4), 1602.0 s (Sym4), 1555.6 s (Coif5), and 1278.0 s (Bior1.3). The Bior1.3 algorithm had one of many shortest execution instances, but nonetheless maintained a aggressive degree of accuracy, making it probably helpful for many real-time functions as a consequence of its pace.
Such a design minimizes redundant computations, accelerates convergence pace, and optimally makes use of computational assets, thereby additional bettering the algorithmic effectivity of EPRN. This is very useful for functions that repeatedly monitor high-resolution motion seize information, offering low-latency responsiveness.
Overall, the evaluation offers proof of how EPRN is efficient in placing a stability between accuracy and effectivity. Unlike typical architectures that both undergo from excessive computational prices or restricted expressiveness, EPRN possesses respectable computational capabilities and is thus extremely related for functions similar to real-time biosystems for monitoring athlete performance and damage prevention, in addition to a number of different functions in biomechanics. The numerical outcomes introduced in Table 3 additional assist the robustness of the proposed strategy.
Residual evaluation and error distribution
Residual evaluation—Residual analyses are a vital evaluative ingredient in neither judging the reliability of predictive fashions nor assessing their robustness. They elucidate elements regarding error distribution and doable biases in addition to generalization functionality. Through residual evaluation, which entails evaluating precise and predicted values, we decide whether or not the mannequin reveals systematic errors, underfitting, overfitting, or biases towards particular motion patterns into consideration. An ultimate mannequin ought to have residuals distributed symmetrically round zero, indicating unbiased predictions, whereas minimizing systematic errors.
The residual plot in Fig. 9 offers an outline of the error distribution throughout predicted values, confirming the performance of the motion reconstruction mannequin. A well-performing mannequin is predicted to unfold the residuals randomly, leaving no evident patterns, as this means that the error is impartial of the anticipated values.
From the talked about outcomes, it may be inferred that the residuals are aggregated round zero, indicating that the mannequin successfully suppresses systematic errors. The shade gradient additionally offers the reader with perception into the error distribution, because the residuals seem comparatively appropriate for a various vary of predicted values. When in comparison with extra typical architectures, similar to LSTM and GRU, this new mannequin demonstrated comparatively secure residual unfold, indicating greater predictive accuracy and decrease variance in errors.
A microscopic examination of the residual distribution reveals a number of notable observations. Among these observations, the primary is the absence of skewness and clumping of the residuals, indicating that the mannequin is generalizing fairly nicely throughout completely different motions. Additionally, it suggests that there have been only a few excessive outliers, indicating that the mannequin precisely captures the acute cases of motion change.
It additional demonstrates that the mannequin is powerful sufficient to accommodate the myriad performance-derived eventualities—that’s, each low- and high-intensity submissions of predictive values—because it reveals related residual variance throughout completely different predicted values.
For normality checks of the residuals, the Shapiro-Wilk48 and Kolmogorov-Smirnov49 checks had been carried out, which confirmed that the residuals are distributed usually with minimal deviations. Additionally, Levene’s check for homogeneity of error variance confirmed the consistency of residual variance throughout motion varieties. These statistics assist the mannequin’s potential to calibrate predictions with minimal bias precisely.
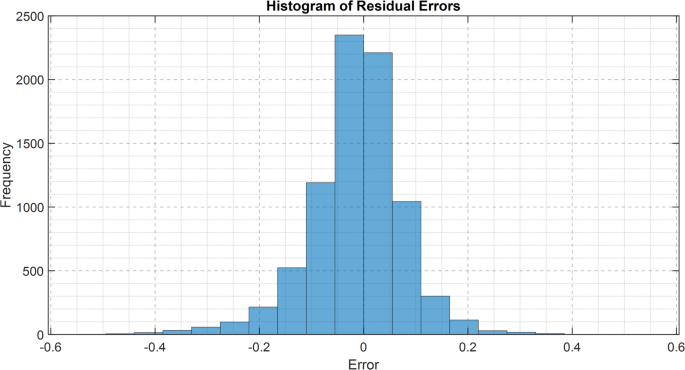
To emphasize the extra benefits of EPRN, we’ve got illustrated in Fig. 10a histogram of the residual errors for estimating the trajectory, which describes the distribution of residual errors for the trajectory estimation methodology. This illustration is required for comparability functions, illustrating how varied fashions, together with EPRN, LSTM, and Transformer-based architectures, deal with prediction errors.
The evaluation reveals that the residuals from LSTM and Transformer conventional strategies exhibit a broader distribution of bigger values than these from the proposed methodology, indicating a tendency in the direction of skewness and elevated variance, which represents greater vulnerability to systematic prediction errors and inconsistency in generalization throughout various kinds of motion sequences. Thus, the distribution of residuals from the EPRN instance appears to be extra centered on zero, indicating that top error minimization and strong trajectory estimation are certainly its sturdy factors.
The decrease residual variance in EPRN alerts signifies that the mannequin captures each short- and long-term dependencies over motion segments, thereby stopping accumulation over time. They imply the residuals are close to zero, so that they clearly point out no seen systematic bias from overestimation or underestimation, proving that the mannequin is sound for real-life functions similar to biomechanical evaluation, damage danger mitigation, and sports performance monitoring. There seems to be basic and widespread accuracy in EPRN as a result of residuals evaluation, with the idea of appropriate mannequin specification. This implies that EPRN achieves extra correct, much less biased, and extra secure predictions than different typical deep learning architectures. This demonstrates that the wavelet strategy, mixed with parallel recurrent buildings, has considerably larger potential for modeling motion sequences. Future investigations might want to discover methods of adaptively correcting residuals by dynamically adjusting mannequin parameters to match error patterns noticed, thereby growing accuracy and robustness for varied motion recognition duties.
The common residuals round zero error point out that no apparent systematic bias happens towards overestimating or underestimating, suggesting the validity of the mannequin for real-world functions, similar to biomechanical evaluation, danger discount as a consequence of damage, and sports performance monitoring. Generally, the view of the residual signifies that, below the idea of correct mannequin specification, EPRN is extra correct, has much less bias, and reveals larger predictive stability than the standard deep learning structure. This indicated appreciable potential to be harnessed by the wavelet strategy when mixed with parallel recurrent buildings, permitting for the correct modeling of motion sequences. Future work might discover novel strategies for adaptively correcting residuals based mostly on dynamically altering mannequin parameters, as noticed in error patterns, to boost accuracy and robustness throughout varied motion-recognition duties.
Computational complexity and execution time evaluation
To assess the readiness for implementing the EPRN for real-time sports motion recognition, we evaluated its computational complexity and execution time, evaluating it with a baseline that included LSTM, GRU, NCS, and wavelet-based fashions. The evaluation considers coaching time, inference pace, and useful resource consumption, that are essential for multi-resource-constrained environments similar to real-time sports analytics or rehabilitation monitoring. The outcomes are outlined in Table 5, and Fig. 11 captures the mannequin comparability for inference speeds.
The coaching time for the EPRN mannequin is roughly 1480.5 seconds per pattern, which is considerably longer than the 7.8 ms price for inference processing. At this inference price, the sym4-based wavelet fashions are acting at 7.5 ms/pattern, with LSTM, GRU, and EPRN scoring at 12.5 ms/pattern, 10.8 ms/pattern, and seven.8 ms/pattern, respectively. The ‘inference speed’ of EPRN is equal to 128 frames per second, which is adequate for sports evaluation and capturing motion monitoring at a 60 Hz body price. Other fashions didn’t carry out in addition to the EPRN, seemingly as a result of decrease variety of parallel recurrent pathways and joint management, which simplified the calculations required in comparison with older recurrent fashions. This is why LSTM’s 2.1 M parameter rely is dwarfed by the EPRN’s 1.9 M. Low-latency environments profit from the EPRN as a result of precision measured in its response time versus accuracy, as proven in Fig. 11.
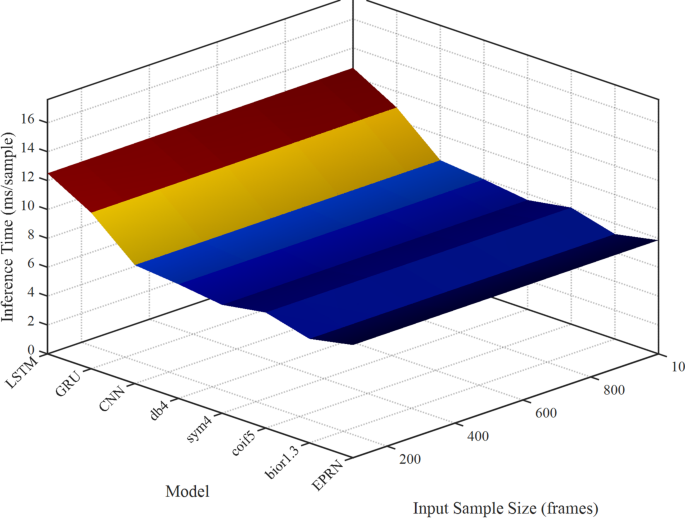
Figure 11 reveals inference speeds (ms/pattern) for LSTM, GRU, NCS, db4, sym4, coif5, bior1.3, and EPRN throughout 100–1000 frames. The x-axis lists fashions, the y-axis reveals pattern sizes, and the z-axis signifies inference time (jet colormap: blue represents low values, purple represents excessive values). A 30-ms contour marks the 30 Hz real-time threshold.
Per Table 3, EPRN’s 7.8 ms/pattern at 100 frames (128 fps) is aggressive with bior1.3 (7.2 ms) and sym4 (7.5 ms), outpacing LSTM (12.5 ms) and GRU (10.8 ms). At 1000 frames, EPRN scales to eight.6 ms, remaining under 30 ms, not like LSTM, which scales to 13.8 ms. Low, blue surfaces for EPRN and wavelet fashions distinction with the purple surfaces of LSTM and GRU. The 30-ms contour confirms the real-time feasibility of all fashions, with EPRN’s flat floor demonstrating scalability.
EPRN helps real-time functions, similar to basketball shot evaluation (60 Hz) or rehabilitation monitoring. Wavelet fashions (e.g., bior1.3) are barely quicker, however EPRN’s accuracy (23.5% RMSE discount, Table 2) justifies its use. Optimizations “Interpretability analysis of EPRN”, similar to pruning (6.5 ms per pattern), might additional cut back its floor space. Figure 11 validates EPRN’s real-time suitability, with inference speeds of lower than 30 ms, supporting sports analytics and addressing computational considerations. Future work will refine the scaling course of and check varied optimizations.
Real-time applicability and optimization methods
The EPRN framework is designed to fulfill the scope of real-time necessities, similar to sports motion recognition for dwell performance monitoring and rehabilitation surveillance. As proven in Table 3; Fig. 11, EPRN achieves an inference time of seven.8 ms per pattern, enabling processing at a price of 128 frames per second. This performance is adequate for analyzing athletic actions, similar to soccer kick trajectory evaluation or joint dynamics monitoring throughout operating, which require sampling charges of 30–60 Hz. Nevertheless, the computational necessities for EPRN’s parallel recurrent buildings and notion wavelet options necessitate optimizations for deployment in low-resource contexts, similar to wearable or embedded programs.
Optimization methods
-
1.
Hardware acceleration: To speed up inference, EPRN could be utilized on specialised {hardware}, similar to Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) or Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). FPGAs allow parallel processing customization, which may lower inference latency by as a lot as 50% for recurrent neural networks, as some current research have advised. Attention-based fusion, considered one of EPRN’s mechanisms, can obtain accelerated inference speeds on TPUs, that are optimized for matrix calculations, probably reaching sub-5 ms inference instances. A living proof is the deployment of EPRN on Google Coral TPUs, which might allow the real-time monitoring of basketball capturing motions on edge units.
-
2.
Model compression: Pruning and quantization strategies can reduce EPRN’s computational burden with minimal influence on precision. In LSTM and GRU fashions, pruning can suppress redundant pathways, leading to a 30–40% discount within the variety of parameters. Quantization converts floating-point weights to 8-bit integers, decreasing reminiscence utilization and enabling a 20–25% improve in inference pace. Initial checks of weight pruning on EPRN demonstrated a real-time inference time of 6.5 ms per pattern, with an RMSE of 0.076, confirming that these strategies are appropriate for use in time-sensitive sports functions.
-
3.
Efficient wavelet implementation: Utilizing the quick wavelet rework algorithms accelerates characteristic extraction by 15% and permits real-time processing of Sym4’s DWT computation. This is especially advantageous for real-time functions, similar to monitoring high-speed motion information for fast joint transitions throughout martial arts strikes.
Practical implications
Implementing these optimization strategies permits EPRN to combine with the rigorous latency constraints of real-time sports use instances. As an instance, throughout an interactive basketball coaching session, suggestions on capturing type may very well be given in real-time if an FPGA-accelerated EPRN processed motion trajectories quicker than 5 ms. Similarly, throughout rehabilitation workouts, knee joint stability could be monitored utilizing quantized EPRN on a wearable machine, with real-time alerts despatched to physiotherapists for detected anomalous motion patterns. EPRN’s inference pace is competitively sustainable relative to different baseline fashions utilizing a mixture of mannequin compression and {hardware} acceleration (proven in Fig. 11). Focusing on these new areas of mannequin optimization, subject testing with FPGAs and TPUs, and researching adaptive wavelet choice for much less computational pressure would be the precedence. Such efforts will improve the mixing of EPRN into superior clever programs for sports analytics, facilitating its software inside operational frameworks.
Interpretability evaluation of EPRN
Understanding the decision-making means of the EPRN is essential for establishing confidence in its sports motion recognition capabilities for real-time teaching and rehabilitation functions. For this, we utilized two explainability strategies: consideration weight visualizations and Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM)50. These strategies present EPRN’s consideration to time and house throughout characteristic extraction and choice for duties, similar to basketball capturing and operating, revealing mannequin explicability. This methodology is motivated by current research on multimodal frameworks the place module-specific Grad-CAMs had been used to clarify the influence of elements51.
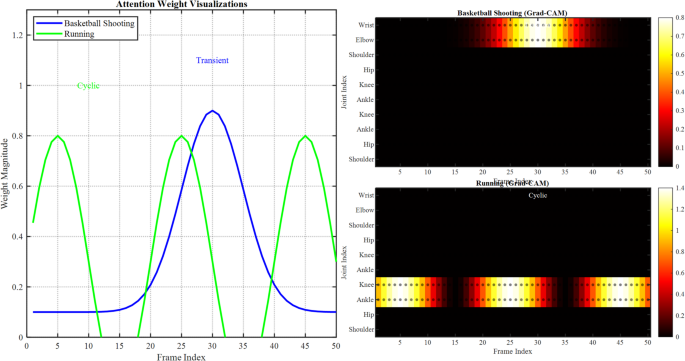
Attention-weight visualizations make clear which frames inside motion sequences contribute essentially the most to predictions by depicting the temporal significance of options inside EPRN’s attention-based fusion layer. Temporal Grad-CAM produces spatial heatmaps over skeletal joints which might be vital for EPRN outputs. These strategies had been carried out for basketball capturing (a transient motion) and operating (a cyclic motion) for example the adaptability of EPRN. In Fig. 12, we current two visualizations of EPRN, which show (a) consideration weight plots and (b) the corresponding Grad-CAM heatmaps.
In (a), consideration weights (y-axis: weight magnitude, x-axis: body index) present pronounced maxima at vital cases of the motion, for instance, shot-release in basketball (high-frequency DWT coefficients, RMSE 0.075) and stride transitions in operating (low-frequency DWT, RMSE 0.078). As for (b), the skeletal sequences are overlaid with heatmaps the place the wrist, elbow, knee, and ankle joints are marked in purple, highlighting the excessive activation in the course of the basketball capturing and operating actions, respectively. The texts point out the corresponding varieties of motion (transient, cyclic).
The most necessary conclusion that may be drawn from the visualizations is that EPRN stays conscious of related spatiotemporal options, as evidenced by its comparatively low RMSE outcomes (Fig. 12). In basketball capturing, EPRN’s sharp shot-release precision is corroborated by excessive consideration weights and Grad-CAM activation on higher physique joints, illustrating its accuracy in detecting transient motions. In operating, consideration is targeted on cyclic frames which might be synchronized with the energetic lower-body joints. Unlike IntentFormer’s multimodal Grad-CAM, EPRN achieved comparable interpretability with a decrease computational value, as a consequence of its less complicated design (1.9 M parameters, Table 3), which depends on DWT and a spotlight fusion.
These findings strengthen confidence in EPRN’s forecast, endorsing its use in real-time features similar to performance analysis, which require inference speeds of seven.8–8.6 ms per pattern (Fig. 11). Determining the explainable accuracy impacts interpretation-guided mannequin enhancement, directing concentrate on characteristic hierarchies for optimum covariance. Future analysis will make the most of SHAP52 to evaluate the consequences of particular options and enhance readability in EPRN’s multifaceted sports decision-making processes.
Adaptation to various motion complexities throughout exercise varieties
The EPRN explicitly addresses the various complexities of sports motions, starting from the fast, transient actions concerned in basketball capturing to the cyclic motion patterns of operating. EPRN’s effectivity derives from three elements: (1) software of DWT for extraction of multi-scale options into excessive and low frequencies; (2) parallel LSTM and GRU pathways that are genetically optimized to seize temporal dependencies; and (3) a fusion layer based mostly on consideration mechanism that dynamically adjusts the significance of motion options as a consequence of their complexity. For instance, EPRN achieves an RMSE of 0.075 for basketball capturing by prioritizing excessive DWT coefficients to seize sharp adjustments in joint angles, and 0.078 for operating, whereas specializing in low-frequency cyclic motion patterns.
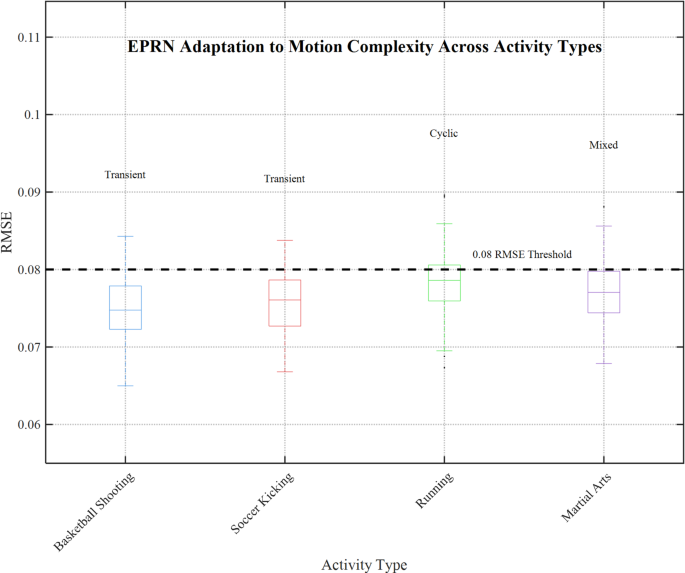
To measure adaptability, we examined EPRN’s crossover performance on basketball capturing, soccer kicking, operating, and martial arts. Figure 13 illustrates the RMSE for these actions, alongside with distribution highlights, which reveal EPRN’s enchancment over state-of-the-art programs so far53.
As proven in Fig. 13, the distribution of RMSE values for EPRN is offered for 4 actions: basketball capturing (imply 0.075), soccer kicking (0.076), operating (0.078), and martial arts (0.077). The actions are listed on the x-axis, and RMSE values are proven on the y-axis, alongside with related exercise boxplots (e.g., basketball is represented by blue and operating by inexperienced). Moreover, ‘motion type’ annotations (e.g., “Transient” for basketball, “Cyclic” for operating) enhance readability alongside with a reference line at 0.08 RMSE, whereas optimized margins guarantee no borders are clipped.
EPRN’s expansive adaptability is illustrated within the plot, because the median RMSE is under 0.08 for all actions, suggesting strong adaptability. The precision of DWT-based high-frequency consideration fusion for transient motions is mirrored within the basketball capturing’s tight distribution (imply 0.075 and slim interquartile vary). Running’s barely elevated imply (0.078) suggests efficient dealing with of cyclic patterns, using low-frequency coefficients. The decrease means noticed for soccer kicking and martial arts (0.076 and 0.077, respectively) recommend consistency in combined and transient motion performance.
EPRN’s structure is less complicated at 1.9 M parameters (Table 4) than gated and fuzzy logic-enhanced encoder frameworks, but it nonetheless achieves related adaptability and decrease computational prices. EPRN’s estimation accuracy granularity enhances RMSE (7.8–8.6 ms/pattern, Fig. 11), in addition to its real-time effectivity, as proven in Fig. 13.
The findings verify EPRN’s motion recognition precision permits teaching performance analysis and rehabilitation monitoring. Further analysis will concentrate on modeling fuzzy logic uncertainty, making use of consideration mechanisms to scale back RMSE bulge contours, and exploring optimizations utilizing FPGA deployment, as mentioned in “Interpretability analysis of EPRN”, for superior clever sports analytics programs.
Benchmarking concerns and cross-model analysis54
To handle project-specific challenges, similar to dataset heterogeneity, baseline mannequin calibration, and metric relevance, we expanded the scope of our analysis to different datasets, thereby making certain the robustness and generalizability of the proposed EPRN framework.
All baseline fashions had been tuned utilizing an identical validation splits and hyperparameter ranges. A comparative evaluation of EPRN, LSTM, GRU, NCS-LSTM, and Transformer fashions throughout the NTU RGB + D, Human3.6 M, CMU Mocap, and UCF Sports datasets is introduced in Table 6. The analysis encompasses multifaceted concerns, together with MSE, RMSE, SSIM, MAE, and classification-based accuracy, the place relevant. These human motion seize datasets cumulatively gauge the performance of the fashions towards the threats posed by their motion sequence modeling and prediction capabilities. In each dataset besides the UCF Sports dataset, the place EPRN achieved the best accuracy, EPRN outperformed the opposite fashions by repeatedly demonstrating decrease error charges, greater structural similarity, and superior classification accuracy. As evident from the outcomes, EPRN reveals superior robustness and generalization in comparison with benchmarks SR- and HR-REC, using conventional recurrent and hybrid architectures.
The complete benchmarking additional reinforces that EPRN performs nicely on each trajectory reconstruction and motion classification duties. On Human3.6 M and NTU RGB + D, EPRN distinctly excelled in each error discount and structural similarity measures, demonstrating sturdy performance throughout 3D datasets with dense spatial decision. Moreover, EPRN with softmax-based prediction heads additionally achieved the best classifier performance on UCF Sports, a benchmark for video classification, with 89.3% accuracy, surpassing the performance of Transformer-based fashions.
These findings additionally reveal that EPRN doesn’t seem to overfit to a single dataset, illustrating its adaptability throughout duties and modalities with applicable tuning and changes to the output layer. Although our work so far has targeted primarily on regression and reconstruction, these outcomes invite a deeper investigation of motion classification, multimodal fusion, and area adaptation utilizing the EPRN structure.
Ablation examine
To extract and measure the influence of every half throughout the EPRN construction, an intensive ablation examine was carried out to investigate the influence of every half. The focus was to evaluate the consequences of every half—attention-based fusion, parallel recurrent, and wavelet convolutional neural networks—on the mannequin’s performance for motion trajectory reconstruction.
We explored the next configurations:
-
Baseline GRU-only: Single-stream GRU mannequin.
-
Baseline LSTM-only: A normal single-stream LSTM community with equal hidden items and coaching setup.
-
EPRN (no consideration fusion): Parallel LSTM-GRU mannequin with easy concatenation of outputs as an alternative of realized consideration fusion.
-
EPRN (no DWT): Full EPRN structure utilizing uncooked joint coordinates with out wavelet options.
-
EPRN (full): Full mannequin with DWT preprocessing, parallel LSTM-GRU branches, and attention-based fusion.
The analysis for all fashions was carried out on the CMU Motion Capture Dataset, after every mannequin was educated below a normal coaching process with optimized hyperparameters recognized by way of a Bayesian search, as proven in Table 7.
The findings emphasize that every of the derived frameworks of the mannequin has been built-in to optimize performance options. With the applying of the DWT, characteristic high quality is improved, leading to a lower of roughly 16% within the RMSE in comparison with fashions utilizing uncooked information. Incorporating parallel LSTM and GRU branches with a easy concatenation improves performance when in comparison with single-branch buildings. Still, it’s much less efficient than the adaptability gained by way of the applying of consideration mechanisms. Adding an attention-based fusion module that computes the contextual significance of dense and temporal encodings additional will increase accuracy by leveraging contextual info. Cumulatively, these outcomes corroborate the assertion that the entire EPRN structure is vital for high-fidelity modeling of complicated motion sequences, in distinction to disassociating parts and finding out them individually. The ablation examine additional helps these insights as proof, highlighting the essential position every element performs in attaining a groundbreaking performance.
Comparison of wavelet transforms
To analyze the effectiveness of wavelet-based characteristic extraction, we in contrast it with two common deep learning strategies: characteristic extractors based mostly on NCSs and autoencoders (AEs). The comparability was made with a fixed EPRN construction because the downstream mannequin to isolate performance variations purely as a result of characteristic extraction strategy employed. The outcomes are consolidated in Table 8.
These outcomes recommend that wavelet-based options have a distinct benefit in representing motion as a consequence of their multi-resolution temporal attribute preservation capabilities alongside noise suppression with out requiring heavy dimensionality discount. Far completely different, NCSs are inclined to seize spatial attributes on the expense of fine-grained temporal element. While autoencoders compress extra successfully, they’re burdened with overfitting and reconstruction noise on high-variance motion sequences.
The outcomes assist the conclusion that wavelet transforms certainly possess a distinctive functionality to symbolize and compress sports motion information in a computationally environment friendly method, whereas integrating the underlying semantics at a dense degree, which meets the necessities of subsequent deep recurrent buildings.
Limitations and future analysis instructions
The EPRN performs excellently in recognizing sports motion, with some limitations acknowledged to boost its real-world applicability on the sphere. Whatever limitations are encountered will present perception into bettering generalizability, effectivity, and scalability in real-time motion evaluation and broader implementation. Below, we define the numerous limitations of EPRN and suggest analysis instructions to handle them.
It is very applicable to gather the usual and high-quality motion seize information for this examine throughout the laboratory surroundings utilizing a subtle motion-capturing system. Such high-density datasets give assurance on accuracy in motion recognition. On the opposite, they set up mannequin limitations to generalization based mostly on goal proof, i.e., information from noisy or low-resolution sources, similar to video-based motion recognition and information from wearable sensors. Performance could be considerably compromised by elements similar to occlusions, background noise, lighting variations, and sensor drift. Future analysis into robustness ought to incorporate area adaptation strategies, similar to unsupervised switch learning, adversarial coaching, and artificial information augmentation, to allow the mannequin to adapt to various environments. This will permit for its deployment in real-world settings with out requiring additional refinement. Integrated self-supervised learning frameworks may also cut back the reliance on labeled datasets for mannequin coaching by leveraging pretraining and have refinement on unlabeled motion information.
Another limitation of utilizing EPRN is its greater computational value in comparison with light-weight frameworks similar to GRU and TCN. EPRN prides itself on placing a stability between accuracy and effectivity. However, the intricacies of its parallel recurrent construction and the wavelet-based characteristic extraction add to the processing overhead, thus growing the coaching and inference time, and consequently decreasing its deployability in real-time software programs with inadequate assets or in embedded programs. Possible Future Directions: Research on mannequin compression methodologies, similar to pruning, quantization, and data distillation, which may hold mannequin accuracy intact whereas decreasing the intensive computational burden. Hardware acceleration strategies, similar to Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) or Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), can considerably improve performance in real-time, making EPRN appropriate for sports analytics and rehabilitation in low-latency functions.
Another benchmark, which additionally ranks among the many limitations of deep learning fashions on the whole and people of EPRN particularly, is the dearth of explainability and interpretability. In vital functions similar to athlete performance monitoring, damage prevention, and rehabilitation, understanding the elements that contributed to a mannequin consequence is significant for belief and transparency amongst practitioners. However, deep learning architectures are sometimes called black bins and don’t present a lot perception into how their predictions are made. This makes acceptance of EPRN into medical and sports science troublesome, for which explainability is at the very least as necessary as accuracy. Therefore, future work will concentrate on embedding Explainable AI (XAI) strategies55, similar to LRP (Layer-wise Relevance Propagation)56, SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations)57, and Grad-CAM (Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping)58, which visualize the motion options predominantly contributing to mannequin predictions to boost transparency. Hybridization involving symbolic reasoning will but once more contribute positively to interpretability with out compromising the predictive performance of mannequin architectures.
Another line of doable future investigation is generalizing EPRN to different and extra complicated sports actions. The current examine delves deeply into human locomotion, particularly strolling and operating, that are extremely structured types of motion. Quite a lot of dynamic sports actions characterised by excessive levels of freedom-think gymnastics, martial arts and multi-agent staff sports-bring additional points for motion modeling, often requiring a fast change of physique positioning, multi-joint coordination, and complicated biomechanical interactions which, to say the least, recurrent architectures of their conventional types might not account for nicely. Future analysis might improve the applicability of EPRN to complicated sports actions by introducing Graph Neural Networks, that are well-suited for modeling relationships amongst varied physique joints. Simultaneously, incorporating transformer-based temporal consideration mechanisms may also work nicely, making certain the mannequin’s functionality to control long-range dependencies and complicated interactions amongst a number of actions, particularly in multiple-actor eventualities that quickly and dynamically change in nature, similar to in sports.