[NAIROBI, SciDev.Net] Despite Africa’s rising digital footprint, the continent’s science and expertise stays underrepresented on Wikipedia, one of many world’s most visited sources of data.
While Africa accounts for round 10 per cent of Wikipedia articles, lower than one per cent cowl science and expertise, Anusha Alikhan, chief communications officer on the Wikimedia Foundation, informed SciDev.Net.
“Only two per cent of Wikipedia editors are from Africa, which complicates the issue, given that the platform receives 50 billion contributions monthly and is read by 15 billion people globally,” stated Alikhan.
“We must become contributors, otherwise the next generation will find us absent from the digital archive of human history.”
Eugene Agbor Egbe, Cameroonian engineer, Wikipedia editor
Between January and June 2025, Sub-Saharan Africa generated 178 million month-to-month web page views on Wikipedia, however this consumption has not translated into African-led content material creation, she added.
Why it issues
Wikipedia has grow to be a worldwide reference level, broadly utilized by college students and journalists and more and more by synthetic intelligence (AI) methods coaching on its huge datasets.
For African science, being absent from this repository dangers invisibility in rising applied sciences corresponding to AI.
|
Keep Science Journalism Alive SciDev.Net offers award-winning science information protection freed from cost. We depend on donations from readers such as you to maintain going. Donate to SciDev.Net right now |
||
|---|---|---|
Cameroonian engineer and long-time Wikipedia editor Eugene Agbor Egbe informed SciDev.Net: “If our data and contributions are missing, Africa will not only be invisible but also dependent on narratives shaped elsewhere.”
The roots of Africa’s underrepresentation lie deep within the continent’s analysis methods, says Job Mwaura, analysis affiliate in cultural anthropology on the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Germany.
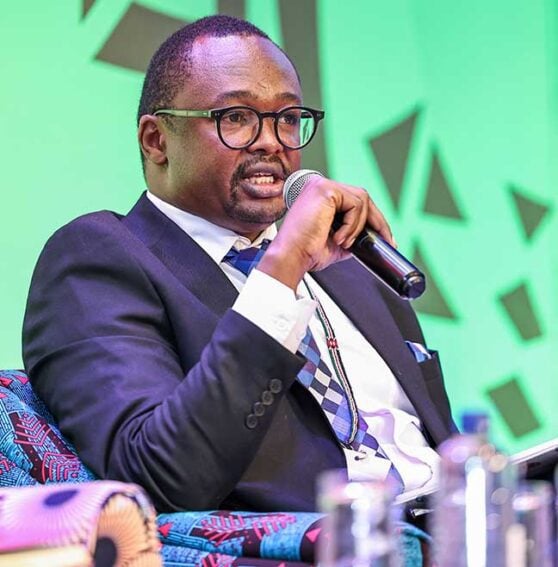

Job Mwaura, analysis affiliate on the division of cultural anthropology at Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Germany. Photo credit score: Duncan Mboya / SciDev.Net
“Western knowledge has dominated Africa through foreign-owned journals that do not favour knowledge from the continent,” he stated.
Mwaura believes the failure of many governments and universities to fund analysis adequately has weakened African voices in international information.
“South Africa is one of the few countries that consistently supports research,” he added.
He says the shortage of funding, coupled with earlier scepticism about Wikipedia’s credibility, has discouraged African scientists from contributing.
1,000 engineers skilled
Egbe, who was not too long ago named Technology Contributor of the Year 2025 by Wikipedia, has been working to vary that. He has skilled greater than 1,000 engineers from 5 African nations to contribute articles highlighting African innovators and scientific breakthroughs.
“I have trained people to write about unsung heroes, groundbreaking research, and innovative projects in Africa’s science and technology sector,” he stated.
Egbe argues that Africa’s contribution to Wikipedia is not only about illustration, however survival within the AI age.
“The rise of artificial intelligence depends on large datasets. If Africa is absent, then AI will replicate those absences and Africa will be left behind,” he defined.
SciDev.Net group member Davis Weddi studying Wikipedia’s Africa page. Wikipedia has grow to be a worldwide reference level, broadly utilized by college students and journalists.
Photo Courtesy of Davis Weddi / SciDev.Net
Africa’s variety presents a possibility to democratise information via native languages.
Wikipedia already hosts 18 African-language editions, with Hausa, Igbo, Yoruba, Somali, and Zulu among the many largest.
Alikhan says African researchers might harness these editions to achieve native communities.
Wikipedia’s Kiwix software program permits offline entry in areas with out dependable web, increasing attain to rural communities.
“Contrary to what many people think, Wikipedia is a secondary source that references primary materials,” Alikhan stated.
“Scientists should use it to make their work accessible to both local readers and global audiences.”
Wikipedia’s credibility
Wikipedia’s credibility has usually been questioned, particularly by lecturers involved concerning the high quality of open-source enhancing.
“Earlier attempts to portray Wikipedia as lacking credibility affected its image, hence leading to low contributions,” acknowledged Mwaura.
But he believes the development has shifted. “Communities and even renowned scientists are now contributing credible, referenced material,” he stated. “The platform has become part of the global knowledge infrastructure.”
For Egbe, the necessity for different African scientists to contribute to the platform is pressing.
“Africa cannot afford to sit back and consume knowledge created elsewhere,” he stated.
“We must become contributors, otherwise the next generation will find us absent from the digital archive of human history.”
This piece was produced by SciDev.Net’s Sub-Saharan Africa English desk.
